Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps provide efficient heating and cooling, offering year-round comfort.
- They are environmentally friendly, reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional systems.
- Modern heat pumps operate quietly and improve indoor air quality.
- While initial installation costs can be higher, long-term energy savings and available incentives make them a cost-effective choice.
Understanding Heat Pumps
Heat pumps have become a popular choice for homeowners seeking efficient climate control. By using electricity to move heat rather than generate it, heat pumps can deliver reliable comfort year-round. Best suited for regions with moderate temperatures, these systems still hold surprising potential even in varied climates across the country. For those who require regular maintenance, upgrades, or quick fixes, Las Vegas, NV heat pump repair services can be invaluable.
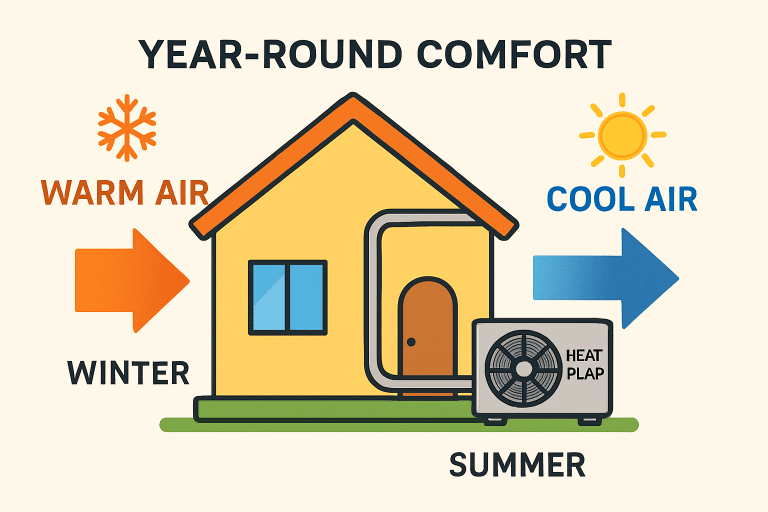
Unlike conventional furnaces or air conditioners, heat pumps work by absorbing heat from one place and transferring it to another. During winter, they extract heat from outside air (or the ground, in the case of geothermal models) and pump it indoors. In summer, the process reverses, allowing the system to expel warm indoor air outside and efficiently keep living spaces cool. These systems can serve as a home’s primary source of heating and cooling, replacing separate HVAC units with a single, energy-saving system.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most compelling reasons to install a heat pump is its remarkable energy efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps use up to 50% less electricity than electric resistance heating systems, such as furnaces and baseboards. Because these systems rely on heat transfer rather than fuel combustion, they incur far less energy waste, which translates directly into lower utility bills over time.
Installing a heat pump may require an upfront investment, but this cost is often recouped thanks to reduced monthly energy expenses. Homeowners can see notable savings, especially when replacing outdated heating and cooling systems. Energy efficiency also means using less power overall, reducing the load on the energy grid, and supporting sustainability goals.
Environmental Benefits
Heat pumps are an environmentally conscious choice for managing indoor comfort. By relying on electricity and ambient heat rather than fossil fuels, these systems emit far fewer greenhouse gases. Researchers at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have found that adopting heat pump technology in residences can cut carbon emissions by 36% to 64%, depending on the system’s efficiency and the home’s insulation. This reduction in emissions is significant as communities aim to minimize their carbon footprint and slow the progress of climate change.
For a deeper understanding of the relationship between heat pumps and long-term climate initiatives, visit the NREL’s report on the benefits of heat pumps. This resource provides insights into how these systems are shaping the future of residential heating and cooling nationwide.
Improved Indoor Air Quality
Heat pumps benefit more than just your energy bill. Their design also contributes to superior indoor air quality. During warmer months, heat pumps naturally dehumidify indoor air as part of the cooling process, helping prevent mold and mildew growth and making conditions more comfortable. During colder months, their consistent operation helps circulate and filter air throughout the home, avoiding stale zones and temperature inconsistencies.
Many heat pump models are equipped with sophisticated filtration systems that reduce common allergens such as dust, pollen, and dander. This can be a considerable asset for families dealing with respiratory conditions or allergies, as cleaner indoor air leads to fewer symptoms and a better quality of life.
Quiet Operation
In addition to efficiency and environmental impact, modern heat pumps are engineered for quiet performance. Traditional heating and cooling systems can create disruptive noise when cycling or blowing air. In contrast, heat pumps operate at much lower volumes, maintaining a peaceful indoor environment. This feature is particularly appreciated in residential areas or settings where noise can affect sleep or concentration.
Considerations and Incentives
Although the initial cost of a heat pump system may seem substantial, it is important to consider available financial incentives and long-term savings. Federal, state, and local programs frequently offer rebates, tax credits, and other incentives to help offset the cost of purchasing and installing energy-efficient equipment. For example, the Inflation Reduction Act currently provides a 30% tax credit for qualifying heat pump installations, making this advanced technology more accessible to homeowners across a range of economic backgrounds.
Homeowners should also factor in the system’s life-cycle costs, including maintenance and repairs, when considering an upgrade. In many situations, the overall savings from reduced energy usage and potential rebates offset the initial investment within just a few years.
Conclusion
Heat pumps provide a comprehensive solution for year-round comfort, offering consistent heating and cooling while delivering substantial environmental and financial benefits. Their energy efficiency, lower emissions, improved indoor air quality, and quiet operation make them a forward-thinking choice for today’s homeowners. With a growing array of financial incentives available, it is easier than ever to enjoy the many advantages of this modern climate-control technology. For those interested in adopting a sustainable and cost-effective approach to home comfort, heat pumps are a wise investment for the future.

