OpenAI is expanding further into health with ChatGPT Health, a new experience designed to enable people to walk into medical appointments more informed and walk out with clearer next steps. It is able to analyze medical results, cluster symptoms, and recommend questions for you to ask of your clinician, while connecting with electronic medical records and popular wellness apps in order to show relevant insights that are privacy-protected.
What ChatGPT Health Does to Prepare You for Appointments
ChatGPT Health is meant to act as a translator from clinical jargon into everyday language and create coherence out of scattered health data, which the system can turn into a pre-visit briefing that makes sense across points on the care continuum. According to OpenAI, it can interface with electronic medical records and consumer services like Apple Health and MyFitnessPal. That would allow it to interpret lab results in context, summarize changes in sleep or activity, and compile a simple list of what you should discuss at your next appointment.
- What ChatGPT Health Does to Prepare You for Appointments
- Why Better Preparation for Medical Visits Really Matters
- Clinician Input and Safety Guardrails Behind the Tool
- Data Privacy and Security Measures for Health Features
- How Patients May Use ChatGPT Health Before and After Visits
- Limits and Responsible Use of AI in Patient Interactions
- Availability Timeline and Next Steps for ChatGPT Health
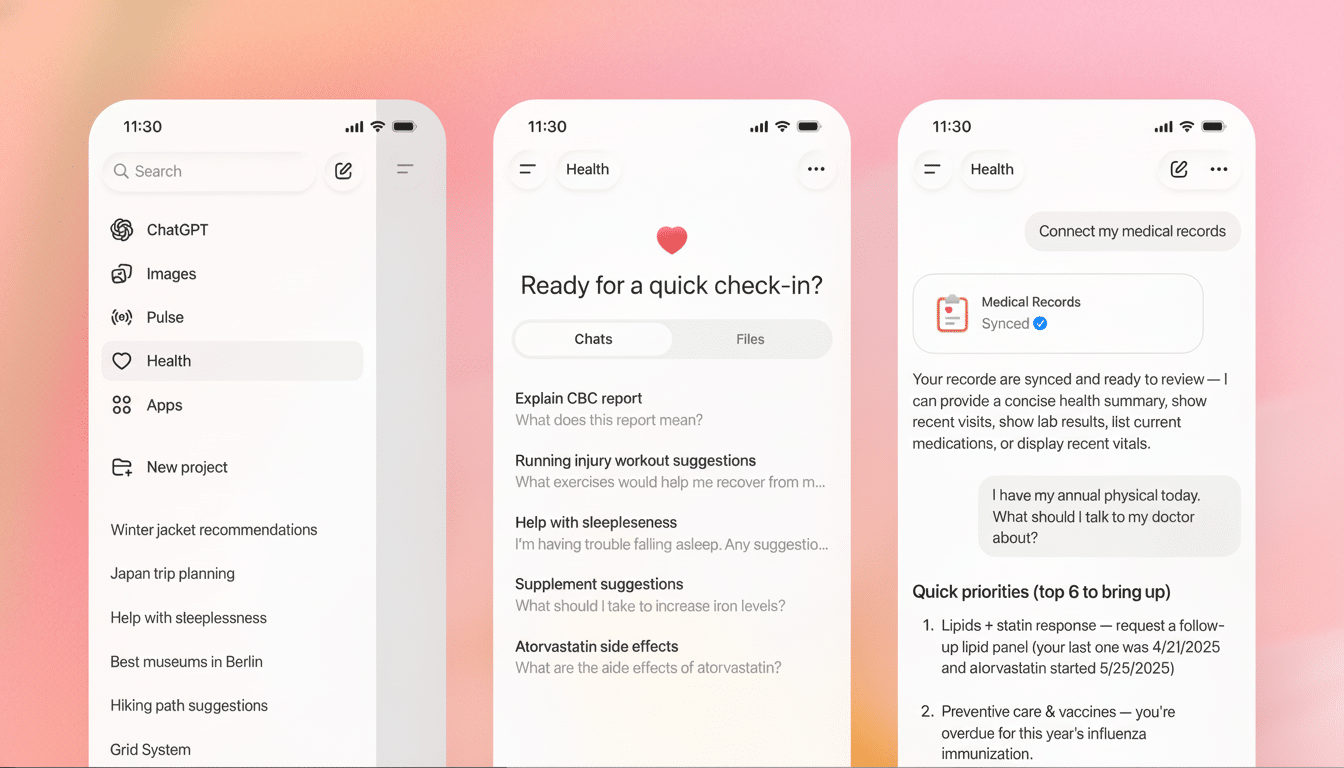
The feature also accommodates post-visit assistance, such as explaining discharge instructions and shooting over follow-up labs and referrals. For what it’s worth, it is designed as an informational tool — not a diagnostic machine — and pushes users to verify recommendations with their clinician.
Why Better Preparation for Medical Visits Really Matters
Primary care visits are short. An average of 18 minutes for the face-to-face is estimated by analyses of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, and many visits include multiple issues. Much of what a patient is told during a visit may be forgotten, and research reviewed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality has found that patients typically remember only about half of what they are told. Lundgren said it’s one reason why many people don’t adhere to medical instructions or recommendations — and why they experience worse health outcomes, including higher mortality rates.
Meanwhile, patient-accessible data has exploded. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT notes that there has been a consistent increase in the availability and use of online medical records since the enactment of the 21st Century Cures Act, which expanded rules about access to information. Yet the volume alone — of test results, portal messages, wearables data — is often overwhelming. A triage tool that prioritizes what’s most important before the visit could help make those minutes count, for both patient and clinician.
Clinician Input and Safety Guardrails Behind the Tool
OpenAI said it worked with over 260 physicians across tens of specialties spread out in 60 countries for two years to craft the product’s responses and safety features. The clinician-in-the-loop approach is designed to cut down on unhelpful or dangerous advice, and to ground explanations in widely shared norms of practice.
The approach mirrors broader findings that AI can be helpful in patient communication. A 2023 study published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that the clinician-rated quality of answers to patients’ questions written by the large language model was generally more empathetic and frequently superior compared to that of doctor responses in an online forum. ChatGPT Health wants to harness that power into organized, visit-ready support without overreach.
Data Privacy and Security Measures for Health Features
Handling health-sensitive information begs privacy questions that truly can’t be avoided. ChatGPT Health incorporates layered safety mechanisms, including specialized encryption and data isolation, OpenAI says — and health data won’t be leveraged to train foundation models. Users can and should enable multi-factor authentication for increased protection.
Integrations with electronic medical records additionally involve HIPAA. Vendors who handle protected health information for covered entities must sign business associate agreements, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights. In practice, that means health systems will be looking closely at how ChatGPT Health stores and handles data, how it maintains audit logging processes, and whether it follows standards such as FHIR for sharing interoperable data.
How Patients May Use ChatGPT Health Before and After Visits
Suppose a patient with new chest pain is on his way to a cardiology appointment. ChatGPT Health would then have in its possession the recent EKG note, cholesterol and troponin results from that portal source, as well as Apple Health activity trends. It could translate “nonspecific ST-T changes” into plain language, focus on patterns that matter for risk assessment, and then turn these into focused questions like side effects of medication to discuss, as well as reminding the patient to bring a list of drugs currently taken and known allergies.
For chronic diseases, it might produce a brief diabetes snapshot before a visit to an endocrinologist — the most recent A1C reading, glucose variability figures taken from a continuous monitor, and a short summary of diet and exercise logs.
The idea is to foster a more efficient, collaborative conversation — not supplant clinical judgment.
Limits and Responsible Use of AI in Patient Interactions
As with any generative model, ChatGPT can get things wrong and sometimes be overly confident. It is not a solution for emergency care or diagnosis, and should not be used to alter medications without consulting a doctor. Regulatory bodies, including the FDA, are still figuring out when AI tools constitute medical devices, and more oversight may accompany new capabilities.
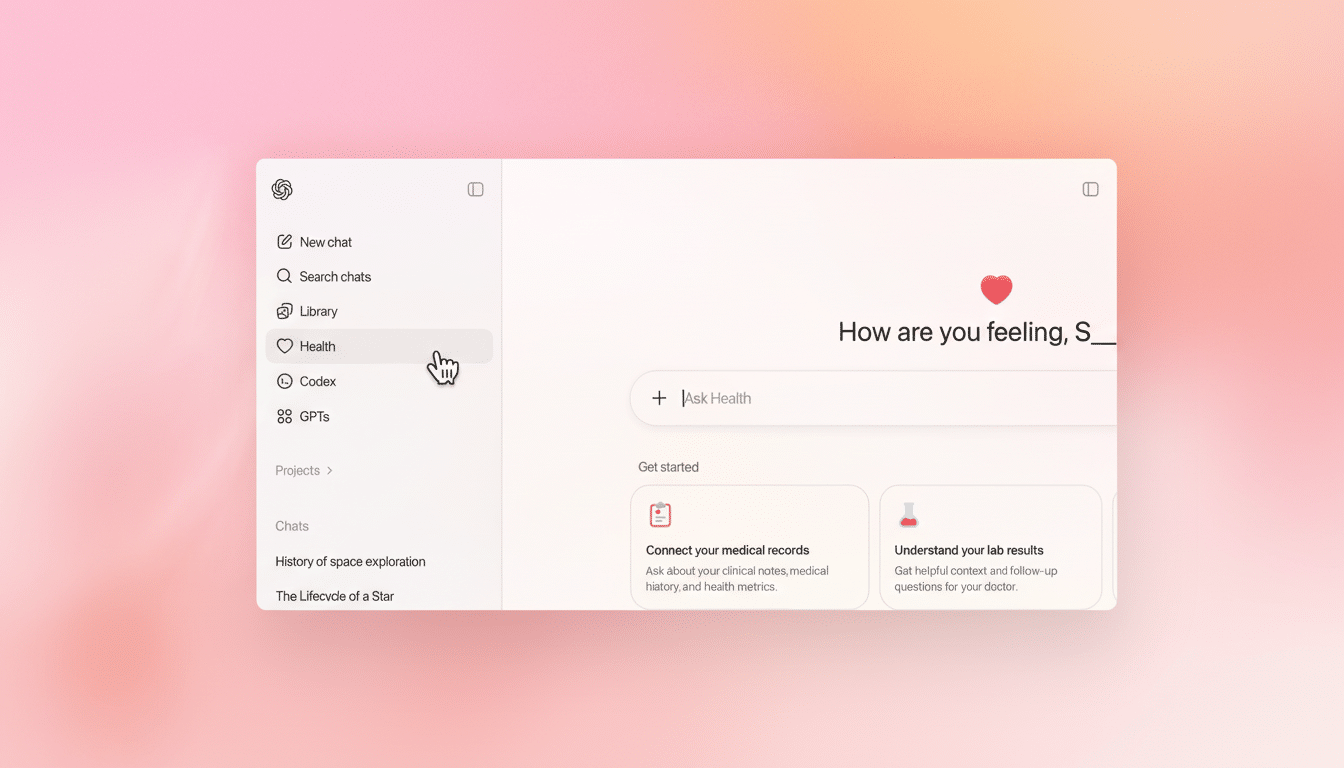
Availability Timeline and Next Steps for ChatGPT Health
ChatGPT Health is being released through a waitlist, with wider availability expected in the weeks ahead. Once activated, users will have a Health option in the sidebar to configure connections and preferences. Look for testing through early pilot programs with health systems and insurers to determine real-world workflows, data-sharing agreements, and measurable outcomes such as improved visit preparedness or fewer follow-up calls.
The promise is simple: tame health data chaos and maximize time in front of a clinician. If OpenAI can provide it consistently, safely, and in cooperation with the medical community, your average appointment might feel less rushed — and a lot more useful.

