Today, Google unveiled Workspace Studio, a brand new approach for organizations to create and distribute AI agents which perform time‑consuming tasks across Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Drive, Calendar and Chat — as well as many popular third-party tools. The big shift: You tell Gemini what you want, and it figures out how to make the workflow — no programming required.
What Workspace Studio Really Does for Teams
Breathe life into your business processes: Workspace Studio empowers employees to create, manage, and publish task‑specific AI agents through natural language. Think of it as an automation command center: outline a workflow, specify triggers and conditions, select the data sources and, behind the scenes, the agent runs. Teams can also share and copy agents that work, so useful automations spread without IT tickets.
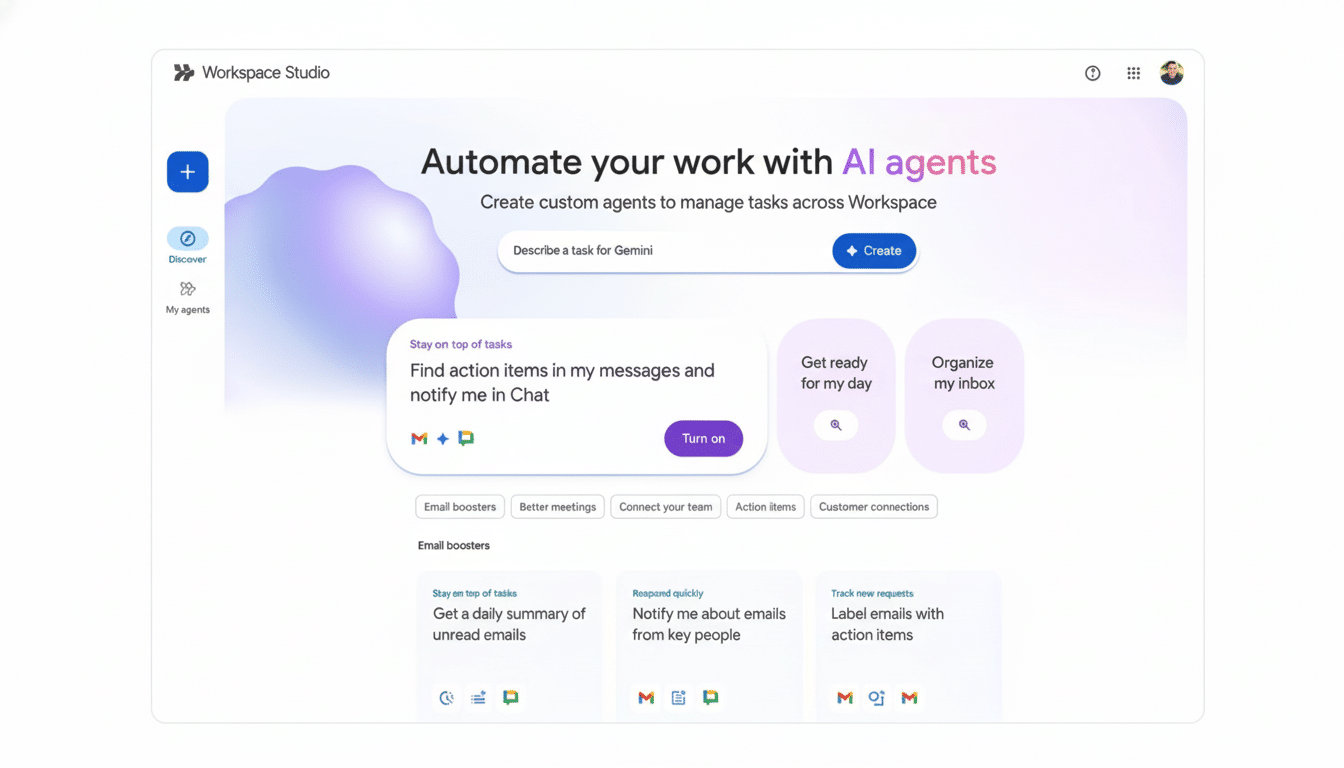
Concrete examples include triaging incoming email by keyword and priority, summarizing lengthy document threads and automatically posting highlights to Chat, logging new leads into a CRM via a form, syncing the status of tasks between Jira and Sheets, or prodding a project channel when a Salesforce opportunity changes stages. Gemini takes care of the orchestration and the glue between services.
This extends Google’s ever-expanding arsenal of AI assistants from NotebookLM for science research and Gemini Code Assist for developers, but Workspace Studio is tailored toward your typical operational work — those unrelenting, unglamorous tasks that suck hours out of your day.
No-code Meets Enterprise Integrations and Apps
Agents crafted in Workspace Studio can reach out beyond Google apps via connectors to services like Asana, Jira, Mailchimp and Salesforce. Early feature commitments include enhanced job-hook capabilities, as well as broader options for sending emails beyond a single domain, which can be important when following workflows that traverse multiple business units or outside partners.
The temptation is obvious: non‑technical staff can perform automation on tasks that previously would have needed tailored scripts or RPA deployments. The move is also one that places Google right in the current of where Gartner has projected low‑code and citizen development as growing across enterprises. McKinsey forecasts generative AI could yield $2.6–$4.4 trillion in new annual economic value by speeding up knowledge work — some of it involving coordination tasks such as email, documentation, and status updates that Workspace agents are meant to automate.
But where most automation tools lean heavily on hard-coded rules, Gemini can parse natural language, summarize context and make structured decisions — taking messy inputs and transforming them into manageable data. That translates into less time spent translating business intent into technical logic, and faster iteration when processes change.
Security and Governance as Standard in Workspace
As a layer on top of Google Workspace, Workspace Studio inherits the host platform’s identity, access and data protections. Administrators can maintain control over who creates or shares agents, see what’s happening and set data loss prevention policies. OAuth scopes and granular permissions can also prevent agents from accessing unauthorized data sources, while audit trails make it simpler to demonstrate how an automation treated sensitive information.
For regulated environments, the promise is that automations run in a compliance envelope (or boundary) equivalent to core Workspace services, which are themselves audited against industry standards like ISO 27001 and SOC 2.

That story of governance is going to be the deal-maker for IT leaders, who are balancing speed and control.
Availability and Usage Limits for Workspace Studio
Workspace Studio is launching to business, enterprise and education customers, for instance, those who are also signed up for Google AI Pro for Education and Google AI Ultra for Business. It’s not available for personal Google accounts.
Google says it’s providing promotional access to higher usage thresholds during the early access phase, and more information about quotas and long‑term limits will be available later. (Although expect there to be some degree of metering that will depend on edition and use case — as is par for the course with AI features linked to model inference and API calls.)
How It Alters Day-to-Day Work Across Teams
The true test is whether employees can offload the drudgery without surrendering accuracy. A sales ops lead might craft an agent that scrapes meeting notes for next steps and pushes tasks to Asana; a support manager could route escalations based on sentiment and product area; and a finance analyst might normalize vendor invoices and flag anomalies to a shared Chat space. Minutes saved per task certainly can add up fast across a company.
Competition is heating up — Microsoft’s got Copilot Studio, Slack has Workflow Builder, while long‑time automation players Zapier and UiPath are embedding generative AI. Google’s advantage is proximity to the documents, emails and calendars where work already exists. By making it easier for companies to deliver reliable automation with Studio, there’s potential for large volumes of what I and others like to call “busywork” to be handed off to agents while still maintaining a human touch somewhere in the workflow.
Bottom line: The goal of Workspace Studio is to make creating AI agents as easy as writing an instruction.
To companies mired in recurring processes, that’s hardly a flashy demo — but rather a concrete path to measurable productivity gains.

