DeepSeek has recently published an experimental version (V3.2-exp) that leverages a new Sparse Attention scheme to reduce long-context inference by roughly 50 percent based on initial internal testing. The open-weight model is hosted on Hugging Face, and the complementary research paper was uploaded to GitHub for fast third-party review.
How Sparse Attention Reduces Inference Costs
Classical attention is computationally expensive with long context, costing the square of the sequence length on average. The DeepSeek method, presented in this work, focuses on limiting the search space before attention to mitigate excessive compute and redundant memory traffic. The model employs a lightning indexer to mark spans in the prompt, and a fine-grained token selector that selects tokens within those spans for a limited attention window.

By using a small, high-value subset of the context, the model uses fewer key–value lookups, reduces the size of the working space on-chip, and in turn increases effective GPU utilization.
Practically, this means you can feed much longer prompts without blowing memory and time budgets—a perennial sore point of applications involving lengthy retrieval-augmented generation such as codebase navigation or legal discovery.
Up to 50% reduction in per-call cost in long-context situations, according to DeepSeek. Although the specific magnitude can be workload- and hardware-dependent, this observation aligns with more than 10 years of research showing that structured sparsity can maintain accuracy while dropping computation, particularly when the selection phase is well calibrated.
What V3.2-exp Means for Developers and Teams
The short-term win is reduced unit economics for context-bound tasks. Imagine doing contract analysis through hundreds of pages, a multi-file code refactor, or clinical summarization on long patient histories. If today a long-context API call costs one unit of work, DeepSeek’s results imply that it could be half as expensive for such similarly structured workloads in the future, potentially allowing budgets to be spent on more throughput or larger contexts.
Because V3.2-exp is open-weight, teams can self-host to save extra with quantization, operator fusion, and kernel-level optimizations. It should similarly interface with existing transformer stacks quite straightforwardly, as the sparse path still exposes a standard attention interface to elements farther down the stack.
A case in point is RAG at scale. Rather than attending exhaustively over an enormous retrieved corpus, the indexer winnows candidates, a selector tightens them up, and focused model compute is directed where the signal lives. That pipeline fits alongside vector databases and retrieval systems that are already part of enterprise stacks.
In the Context of Competing Efficiency Efforts
Sparse attention is one of several methods adopted to bound the cost of inference. FlashAttention is a kernel-level exact attention method for efficient speed and memory. Longformer and BigBird incorporated pattern-based sparsity for complexity reduction over long sequences. Mixture-of-Experts structures use only a small subset of expert blocks for each token to reduce overall FLOPs. Quantization, KV cache compression, and speculative decoding shave additional time and costs.
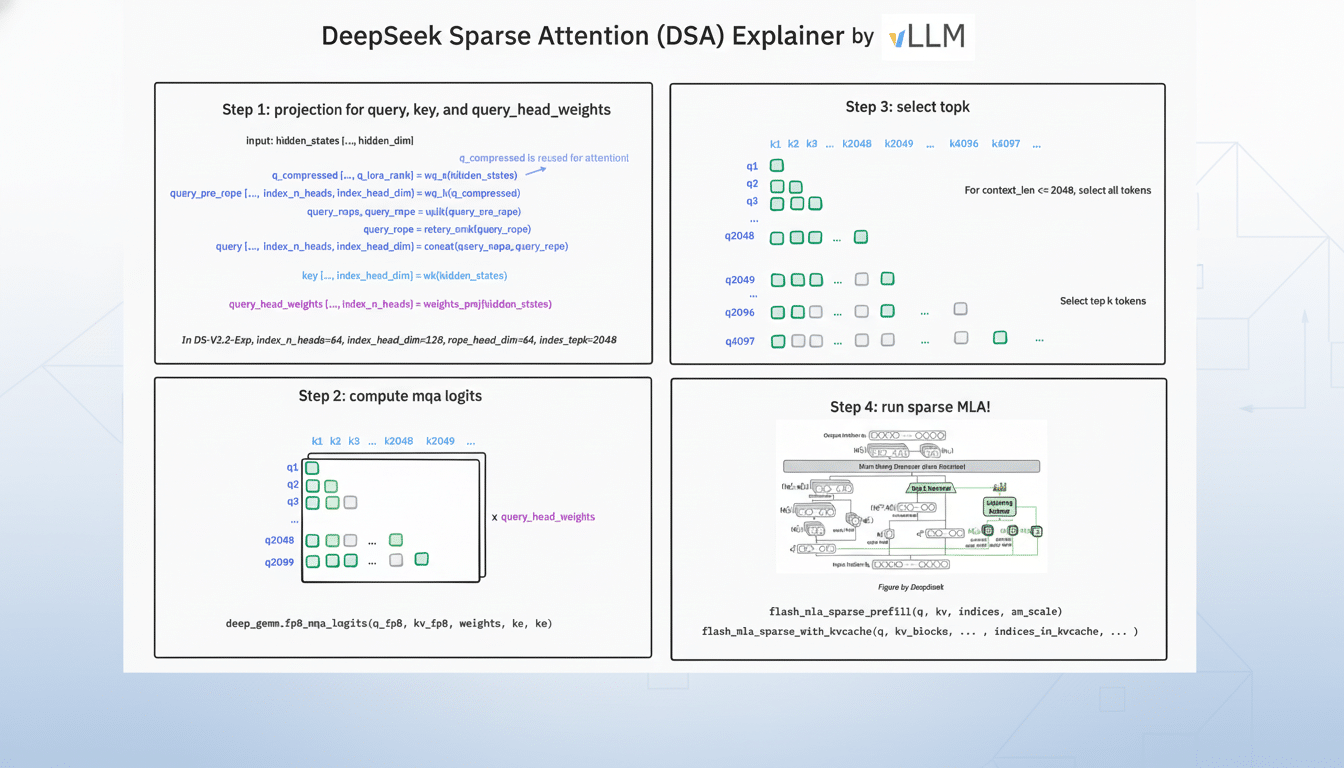
DeepSeek’s approach combines retrieval-like preselection with fine-grained token gating, addressing perhaps the most expensive regime of all—very long prompts. If stand-alone assessments demonstrate similar quality to dense attention on reasoning and recall benchmarks, we could see this turn into a go-to strategy for long-context production loads.
Quality, recall, and risks to watch in sparse attention
Any strategy that is sparse risks ignoring tokens that are important. The lightning indexer and token selector edge very close to the optimal precision–recall balance, particularly on tasks where a single unwarranted clause or variable flips the answer. Benchmarks like Needle in a Haystack, RULER, and L-Eval can validate whether the model remembers information over thousands of tokens.
Then, there’s the issue of adversarial or edge cases. Prompts designed to hide important facts under low-salience text may be able to dodge the selector, and domain shifts may degrade the indexer’s judgment. Look for researchers and enterprise users to exploit these failure modes before they route high-stakes workloads.
Market implications for AI costs and provider strategy
Inference cost is the most significant line item on many AI P&Ls. Cutting spend on long-context calls in half could move the needle on margin for API-first startups or internal AI platforms. For providers competing against firms offering premium pretrained long-context models (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic, Google), a credible sparse attention path is an attractive lever to improve COGS without negative impact on capability.
DeepSeek, which made news in the past with R1 work centering on reinforcement learning–driven efficiency, is once again banking on frugality as a differentiator. By open-sourcing weights and a paper, the company is inviting the community to verify the claims expeditiously—something that tends to expedite iteration and adoption if results are sound.
What happens next for V3.2-exp and sparse attention
Anticipate quick replication by independent labs, including fine-grained ablations of the indexer and selector. Stay tuned for head-to-head results on public long-context benchmarks as well as practical throughput numbers on popular GPUs. If quality continues to be competitive and costs continue to fall, sparse attention could become a standard component of production stacks chasing large prompts, from document AI to developer tooling.
Until then, the commitment is simple and potent: keep the context long, tell the truth, and make the bill smaller.

