Airbnb is moving from pilot projects to a platform-wide AI push, with CEO Brian Chesky outlining plans to embed large language models across search, discovery, and customer support. The company says new conversational tools will help travelers find the right stay faster, plan trips end to end, and give hosts smarter ways to manage listings—while also streamlining internal operations.
From Search Box To Trip Copilot For Personalized Travel
Chesky framed the shift as a step toward an “AI-native” Airbnb where the app learns user preferences and context over time. Instead of forcing travelers to juggle filters and maps, the company is testing natural language search that can parse requests like “quiet beachfront homes with reliable Wi-Fi and a workspace near Lisbon in May” and return ranked, explainable results. The goal is a system that remembers traveler profiles, travel histories, and even accessibility needs to refine recommendations across the entire itinerary.
- From Search Box To Trip Copilot For Personalized Travel
- Monetization Will Follow Experience In Conversational Search
- Support Bots Gain Voice And Reach Across Customer Service
- Data Moat And Engineering Adoption For AI Personalization
- Why This Move Matters Now For Airbnb And Travelers
- What To Watch Next As Airbnb Scales Its AI Initiatives
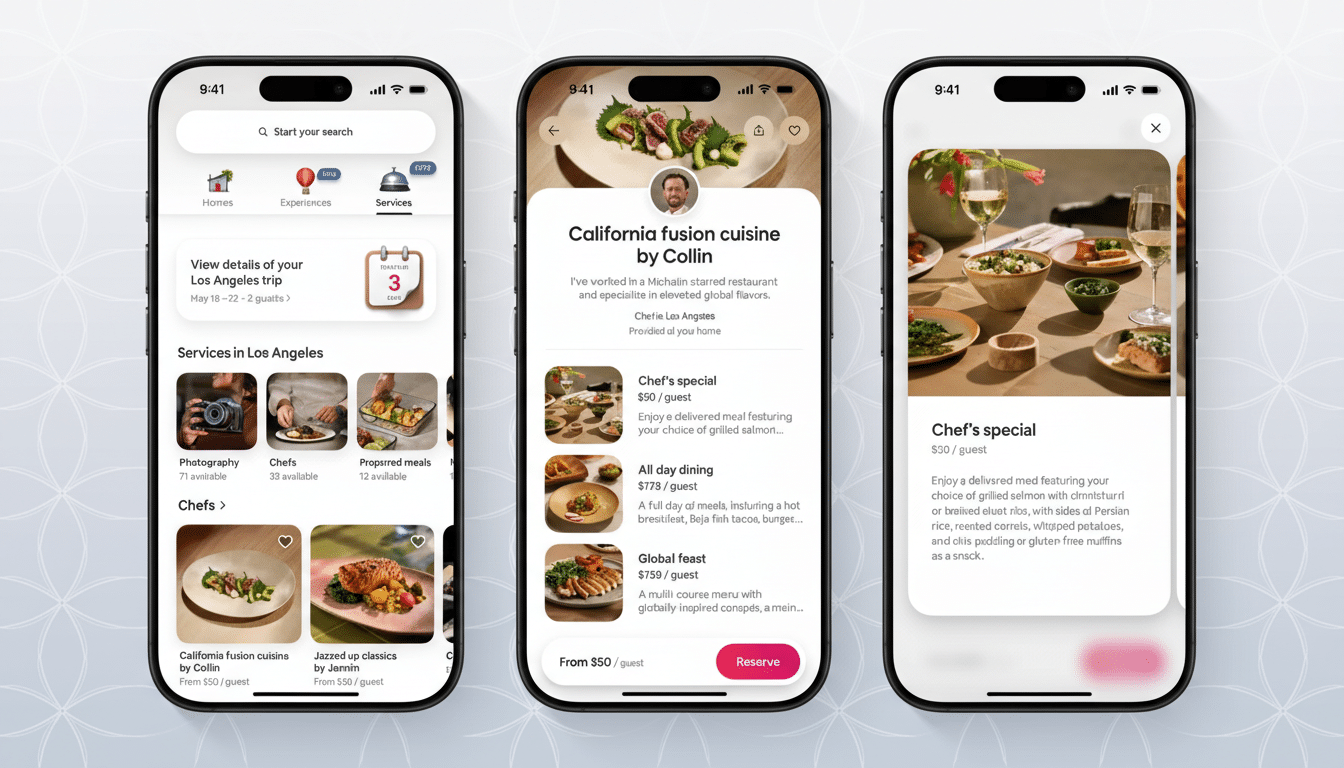
Today’s early version is limited to a small slice of traffic as Airbnb experiments with prompt flows, guardrails, and ranking quality. The company says the feature will “evolve into a more comprehensive and intuitive search experience that extends through the trip,” signaling ambitions beyond simple query matching to itinerary building, neighborhood advice, and activity suggestions.
Monetization Will Follow Experience In Conversational Search
Asked whether conversational search will eventually include sponsored placements, Chesky said design will come first, monetization later. He described potential ad units that feel native to a chat-like flow, avoiding jarring interruptions or distrust. That stance mirrors the broader industry debate: AI assistants promise higher-intent engagement, but blending ads into dialogue raises new expectations for transparency, labeling, and ranking fairness.
Any move into sponsored listings inside AI results will likely require clear disclosures and controls for guests and hosts, along with robust bias testing. Given how ranking already shapes booking outcomes on travel platforms, even small adjustments to conversational recommendations could have outsized effects on visibility and pricing.
Support Bots Gain Voice And Reach Across Customer Service
Airbnb’s existing LLM-powered support bot, launched in North America, now resolves roughly a third of customer issues without human intervention, according to the company. Next up: voice calling and broader language support, with a target of “significantly more than 30%” of tickets handled by AI over time. That expansion will demand careful containment of hallucinations and clear escalation paths—especially in edge cases like last-minute cancellations, safety incidents, and refund disputes where context and empathy matter.
Industry analysts have long projected a growing share of service interactions handled by automation, but travel introduces added complexity because bookings, payments, identity verification, and on-the-ground experiences intertwine. Getting it right could shorten queues for routine issues while reserving human agents for high-stakes cases.
Data Moat And Engineering Adoption For AI Personalization
Key to Airbnb’s plan is its corpus of identity, listing, and review data—signals that can anchor personalization, detect fraud, and ground model outputs. New CTO Ahmad Al-Dahle, previously involved with frontier model efforts at a major social platform’s AI lab, is expected to guide how Airbnb blends proprietary data with foundation models to boost relevance and reliability without compromising privacy or trust.
Internally, the company says 80% of engineers now use AI tools, with a goal of reaching 100%. That uptake aligns with a broader wave of code copilots and automated testing that compress development cycles. The challenge will be governance: standardizing prompts, evaluating model changes, and preventing regressions in ranking or policy enforcement as systems update.
Why This Move Matters Now For Airbnb And Travelers
The announcement arrives alongside stronger-than-expected financials—Airbnb reported Q4 revenue of $2.78 billion, up 12% year over year—giving the company room to invest in long-horizon product bets. It also lands amid an industry race to operationalize generative AI in travel. Booking Holdings has tested conversational trip planners, and Expedia Group introduced an assistant for itinerary support, while online travel agencies experiment with AI re-ranking, bundle assembly, and dynamic packaging.
For Airbnb, the stakes are higher than convenience. Better matching reduces search fatigue, increases guest satisfaction, and can smooth seasonality for hosts by surfacing the right listing at the right moment. Conversely, misfires—biased results, opaque ads, or unreliable support decisions—could erode trust. Expect heightened scrutiny under emerging AI governance regimes, including requirements on explainability and risk controls in major markets.
What To Watch Next As Airbnb Scales Its AI Initiatives
- How quickly conversational search expands beyond the current test cohort, and whether Airbnb publishes quality metrics such as click-through, booking conversion, and dispute rates for AI-assisted sessions.
- The introduction and labeling of any sponsored units inside AI results, plus opt-outs for users.
- Voice support performance across languages and regions, and the company’s safeguards for sensitive scenarios.
- Developer workflow changes as AI tools reach 100% adoption, including model evaluation standards and red-teaming for ranking fairness.
If execution matches the vision, Airbnb’s app could shift from a listing directory to a proactive trip copilot. That promise, however, will be measured not by demos, but by whether guests find better stays with less effort and hosts see more predictable demand—without sacrificing the trust that made the marketplace work in the first place.

