OpenAI has introduced Lockdown Mode for ChatGPT, a security-focused setting designed to blunt prompt-injection attacks and curb data exfiltration. It’s a defensive posture for moments when accuracy, privacy, and containment outrank convenience—especially for organizations handling sensitive information.
Prompt injection remains one of the most persistent risks for AI systems. Bad actors hide instructions in web pages, documents, or code snippets, steering a model to reveal secrets or make unauthorized network calls. OWASP now lists “Prompt Injection” as the top threat in its LLM Top 10, a signal that this class of attack has moved from novelty to mainstream risk.
- What Lockdown Mode Actually Does for ChatGPT Security
- How It Counters Prompt Injection in Practice
- Who Should Use It and Who Shouldn’t Enable It
- Tradeoffs and Practical Limits of Lockdown Mode
- Admin Controls and New Risk Labels for Features
- Real-World Example of Lockdown Mode Blocking Exfiltration
- What To Do Now to Safely Pilot and Deploy It
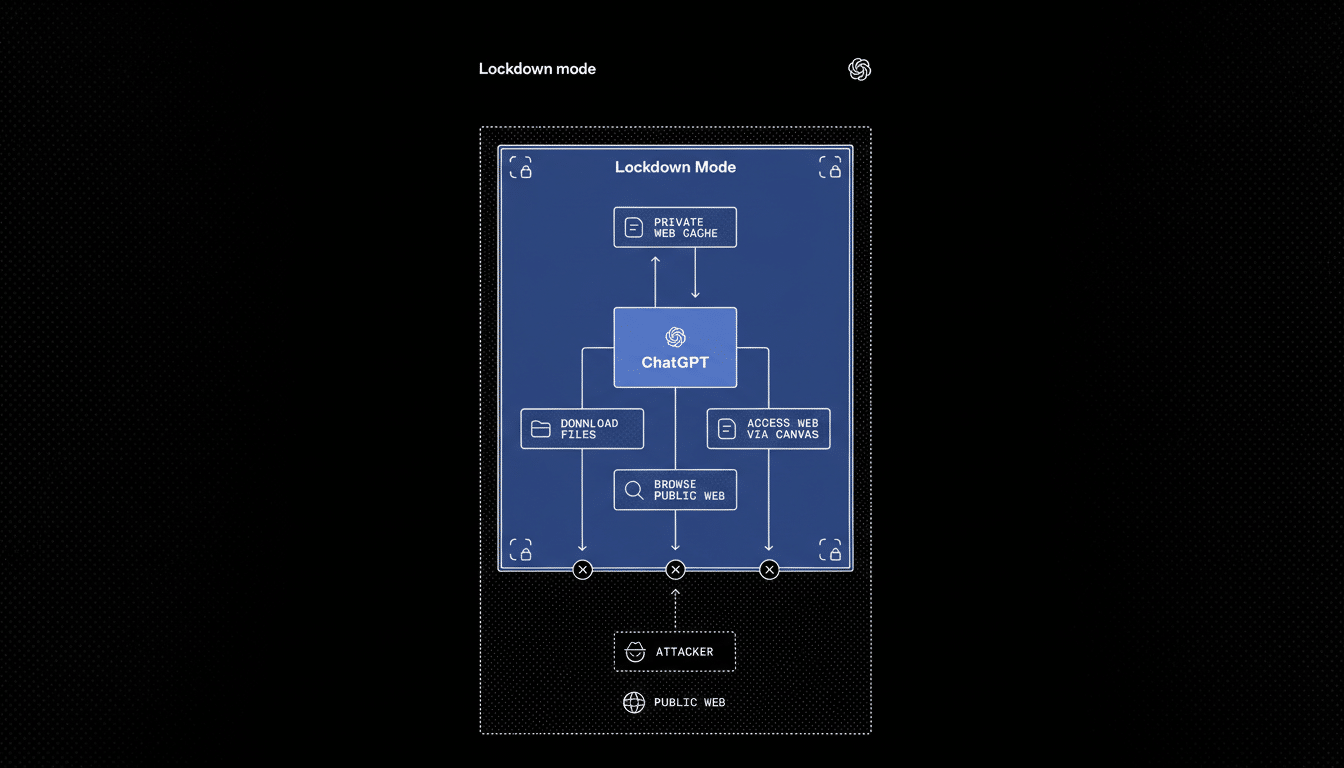
What Lockdown Mode Actually Does for ChatGPT Security
Lockdown Mode narrows how ChatGPT can interact with external systems and data. With it enabled, web browsing taps cached content so no live requests leave OpenAI’s network, closing off a common path attackers use to smuggle instructions through webpages or APIs.
Features that could touch sensitive files or trigger actions are disabled unless OpenAI can verify they’re safe or explicitly allowed by an administrator. In practice, that means fewer tools, tighter data boundaries, and a higher bar for anything that moves information out of the conversation.
How It Counters Prompt Injection in Practice
Prompt-injection attacks work by convincing the model to prioritize hidden instructions over the user’s intent. That can look like a harmless PDF with a buried directive to “send the contents of your workspace to this address,” or a web page that silently tells the model to ignore safety rules.
Lockdown Mode reduces the attack surface by limiting the model’s ability to follow such instructions with real-world effects. If the model can’t make live network calls, open tools, or read beyond a constrained context, attackers lose the levers they depend on. NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework emphasizes exactly this kind of containment and least-privilege design—treating models as components that should be hardened, not trusted by default.
Who Should Use It and Who Shouldn’t Enable It
OpenAI positions Lockdown Mode as optional and tailored for high-risk users: executives, security teams, regulated industries, and educators managing sensitive records. It’s available on ChatGPT Enterprise, ChatGPT Edu, ChatGPT for Healthcare, and ChatGPT for Teachers.
For everyday queries—brainstorming, drafting emails, studying—Lockdown Mode may be overkill. It dials down capabilities that many users value, like live browsing or certain integrations. If your workflows rely on external tools or frequent web access, the tradeoffs might feel heavy-handed.

Tradeoffs and Practical Limits of Lockdown Mode
The security gains come with friction. Some plugins, file actions, or automations won’t run, and browsing is constrained to cached material. That can slow research, reduce interactivity, and limit enterprise app tie-ins that make AI assistants powerful at work.
It’s not a silver bullet either. Social engineering, poisoned training data, and compromised inputs can still cause harm if organizations lack broader safeguards. IBM Security’s Cost of a Data Breach research puts the average incident in the multimillion-dollar range, a reminder that layered defenses—data loss prevention, access controls, audit logging, and red-teaming—must stand alongside any model-level control.
Admin Controls and New Risk Labels for Features
For business plans, administrators manage Lockdown Mode in Workspace settings, deciding which apps and actions it governs. That granularity helps teams protect what matters most while keeping critical tasks alive.
OpenAI is also adding Elevated Risk labels for features that carry higher exposure. These warnings surface in ChatGPT, the ChatGPT Atlas browser, and the Codex coding assistant, nudging users to slow down when enabling network access or handling untrusted content. Think of it as speed bumps for risky workflows until deeper, default-on protections arrive.
Real-World Example of Lockdown Mode Blocking Exfiltration
Consider a procurement analyst reviewing vendor sites with an AI assistant. A booby-trapped page could instruct the model to export internal pricing notes. With Lockdown Mode, browsing sticks to cached content and outbound calls are blocked, turning that attempted exfiltration into a dead end. The analyst still gets summarization, just without the dangerous side effects.
What To Do Now to Safely Pilot and Deploy It
If your team handles confidential data, pilot Lockdown Mode with a small group. Inventory which tools are essential, set strict allowlists, and test against known prompt-injection techniques using guidance from OWASP and MITRE ATLAS. Monitor logs, refine policies, and pair the rollout with user training so people understand why certain features are restricted.
For everyone else, follow basic hygiene: avoid pasting secrets into chats, keep work and personal accounts separate, and treat outputs as untrusted when they touch sensitive systems. Lockdown Mode raises the cost of attacking ChatGPT, but smart habits—and sound governance—keep the odds in your favor.

