California and New York have flipped the switch on the nation’s most stringent AI rules, turning voluntary safeguards into enforceable obligations for the companies building and deploying large-scale models. Legal experts say the shift puts real teeth behind transparency and safety—without yet freezing innovation—while setting up an inevitable clash with federal officials who want a single, lighter-touch framework.
What changes first is accountability. Model developers and major AI platforms must disclose how they intend to curb catastrophic risks, report serious incidents on the clock, and protect whistleblowers who surface problems. The result is a new compliance baseline for any AI company with national ambitions, because ignoring the country’s two most consequential tech markets is not a viable option.
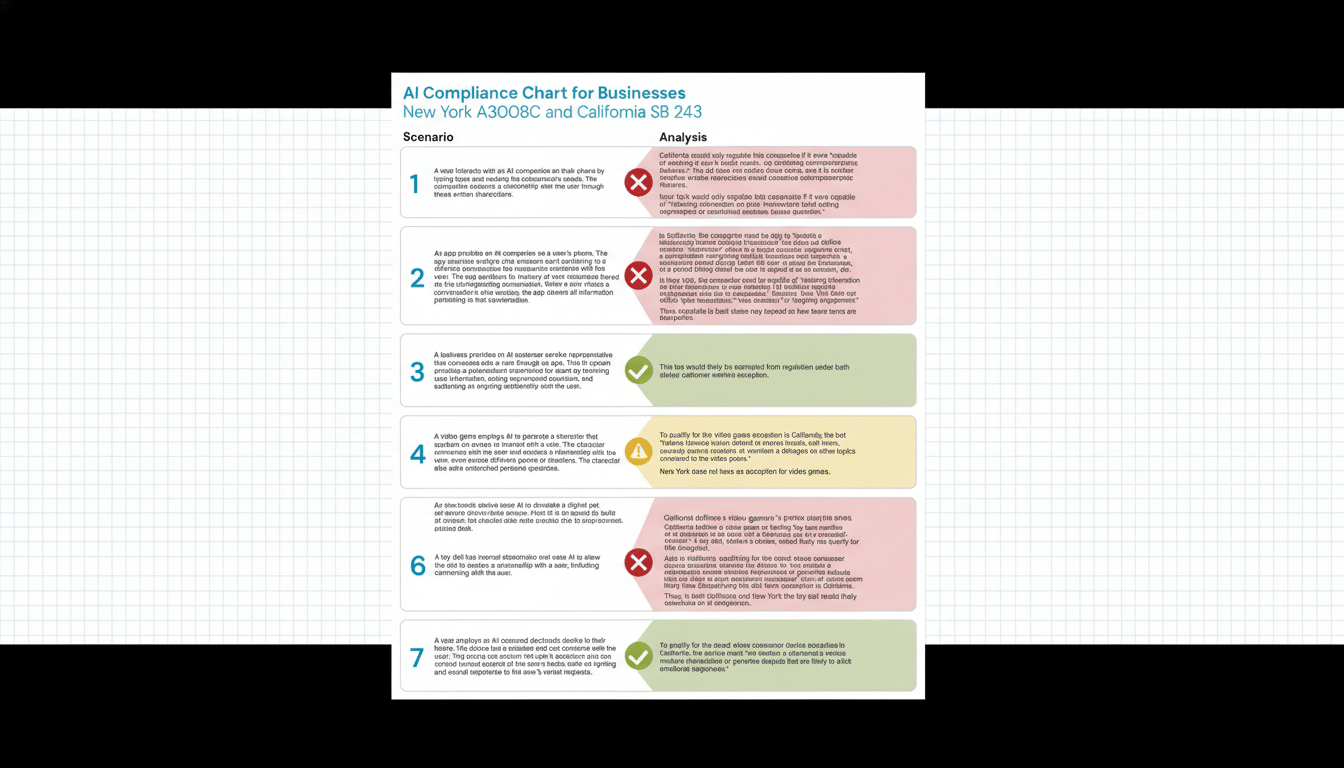
What Changes Under California SB 53 and New York’s RAISE Act
California’s SB 53 requires developers to publish risk mitigation plans for their most capable models and to report “safety incidents”—events that could enable cyber intrusions, chemical or biological misuse, radiological or nuclear harms, serious bodily injury, or loss of control over a system. Companies have 15 days to notify the state and face fines up to $1 million for noncompliance.
New York’s RAISE Act mirrors the disclosure rules but moves faster and goes further on enforcement. Safety incidents must be reported within 72 hours, and fines can reach $3 million after a first violation. It also introduces annual third-party audits, adding an independent check that California does not mandate.
Both laws target firms with more than $500 million in gross annual revenue, effectively pulling in Big Tech and large AI vendors while sparing many early-stage startups. Regulators chose a transparency-first approach after a more muscular California proposal, SB 1047, failed; that earlier bill floated mandatory “kill switches” and safety testing for models above a hefty training-cost threshold.
One provision stands out to corporate counsel: California’s whistleblower protections. Unlike risk disclosures—where many multinationals are already preparing to comply with the EU AI Act—clear, state-level protections for employees who report AI safety issues are unusual in tech and could reshape how firms handle layoffs, investigations, and internal dissent.
Compliance Impacts For AI Developers And Enterprises
In practice, the new rules force a buildout of safety governance rather than a halt to R&D. Companies need incident-response playbooks that define what counts as a reportable AI event, on-call escalation, and evidence preservation. Expect more rigorous red-teaming, centralized logging for model behavior, and formal “safety case” documentation that product teams and counsel can stand behind.
Because many global firms already map to the EU AI Act, legal experts say the marginal lift may be smaller than feared—especially on disclosures. Gideon Futerman of the Center for AI Safety argues the laws won’t change day-to-day research dramatically but mark a crucial first step by making catastrophic-risk oversight enforceable in the United States.
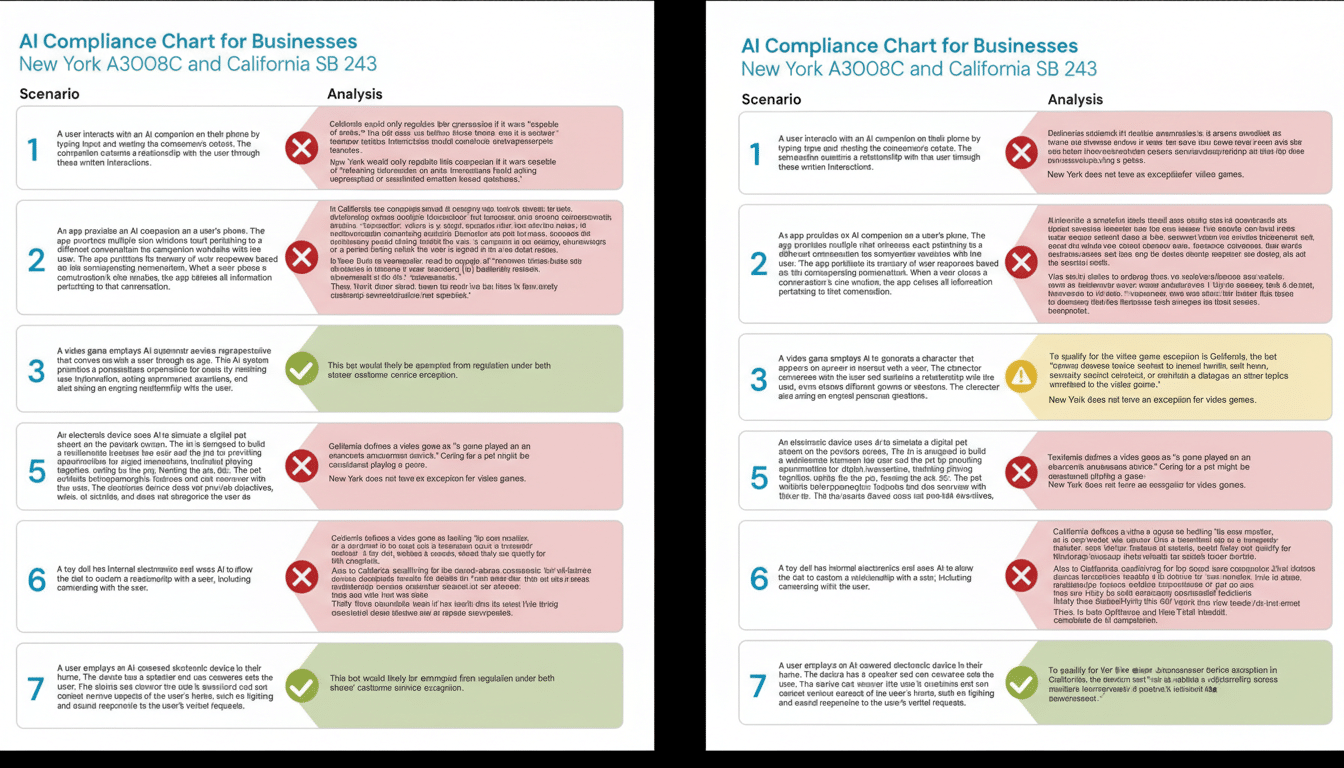
Consider a real-world scenario: a general-purpose model used by a fintech is jailbroken to generate malicious code that compromises a partner network. Under New York’s law, that potential cyber misuse could trigger a 72-hour report and an audit trail; in California, the firm would have 15 days. For enterprises, these timelines now shape vendor contracts, SLAs, and how quickly findings reach the board.
Federal Pushback And The Preemption Question
The administration has signaled a push to centralize AI governance, warning that a patchwork of state rules could slow innovation and create compliance whiplash. The Justice Department is forming an AI Litigation Task Force, according to reporting by CBS News, to challenge state provisions seen as incompatible with a national policy framework.
Yet preemption is not a foregone conclusion. Attorneys point out that, absent a federal statute that explicitly overrides states, courts often allow states to set stricter standards—health privacy under HIPAA is a familiar example. Aside from a new request for information from the Center for AI Standards and Innovation—formerly the AI Safety Institute—Washington has not offered a comprehensive replacement for state-level rules. A recent congressional attempt to block state AI laws failed, underscoring how unsettled preemption remains.
How Strict Are These Rules In Real-World Practice
Compared with the shelved “kill switch” approach, SB 53 and the RAISE Act prioritize transparency and traceability over hard technical constraints. New York’s independent audits raise the bar, but neither state currently mandates third-party model evaluations before release. That leaves meaningful flexibility for labs while making it riskier to ignore catastrophic failure modes—or to bury them.
There is a legal trade-off. The documentation these laws require can surface in discovery or class-action suits. With whistleblower protections in California, companies will need robust anti-retaliation policies and clearer channels for raising AI safety concerns. Investors are already pricing governance, privacy, and cybersecurity readiness into funding decisions, further aligning market incentives with compliance.
What To Watch Next As Enforcement And Challenges Begin
Watch for early enforcement actions, federal challenges by the new task force, and how state agencies define “safety incidents” at the edges. Also track convergence with the EU AI Act; many firms will seek one harmonized control set spanning disclosures, incident response, and audits.
For now, legal experts advise treating these laws as the floor. Build a centralized incident register, expand red-team coverage to catastrophic misuse, log model lineage and fine-tuning data, set board-level risk thresholds, and harden whistleblower and vendor oversight. Transparency alone won’t make systems safe, but California and New York have made it non-optional—and that changes how leading AI companies will operate.

