Linux moves fast, and some once-essential commands are now legacy. Across mainstream distributions, maintainers are retiring aging utilities for better-secured, kernel-integrated tools. If you still rely on the old standbys below, it is time to switch to their modern replacements.
Why These Linux Commands Were Deprecated and Replaced
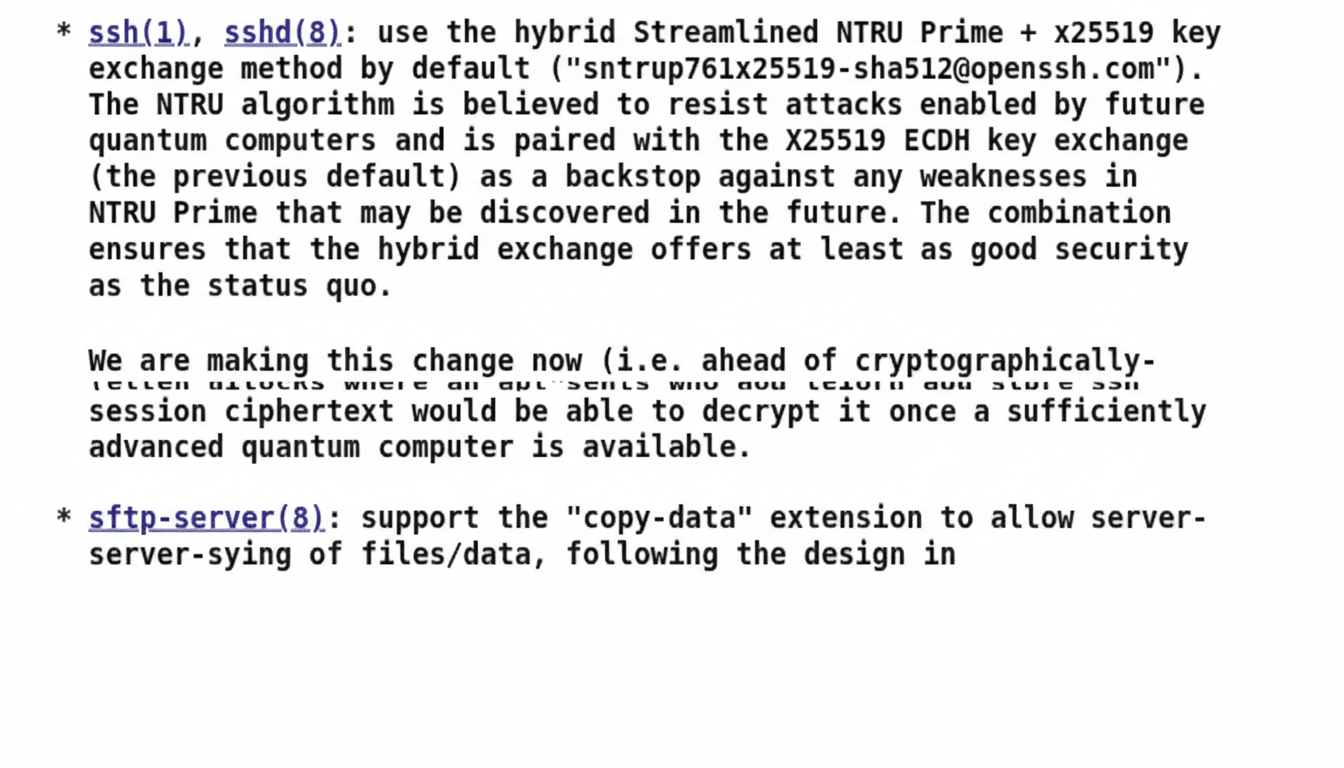
Three forces drove the change: security, kernel integration, and maintainability. The iproute2 suite and netlink interfaces give administrators richer, faster networking control than the old userland tools ever could. Wireless tooling moved from the obsolete Wireless Extensions to nl80211/cfg80211. And in the OpenSSH ecosystem, longstanding scp pitfalls prompted a move to SFTP by default in OpenSSH 9.0, as maintainers documented years of scp parsing issues.
- Why These Linux Commands Were Deprecated and Replaced
- Moving from ifconfig to ip for network management
- Switching from iwconfig to iw for wireless tooling
- Replacing scp with sftp or rsync for safer file transfers
- Use grep -E and grep -F instead of egrep and fgrep
- Replacing netstat with ss for faster socket inspection
- Moving from route to ip route for modern routing tasks
- Switching from arp to ip neigh for neighbor table control
- How to Migrate Without Breaking Scripts and Builds
The result is a cleaner baseline: fewer edge-case bugs, better IPv6 handling, and commands that reflect how the Linux kernel actually manages networking today. Red Hat, Debian, Ubuntu, and Arch Linux documentation all nudge users toward these replacements, and many container images no longer ship the legacy tools by default.
Moving from ifconfig to ip for network management
ifconfig came from the aging net-tools package, which has long been considered legacy. ip from iproute2 talks to the kernel via netlink, exposes far more detail, and is actively maintained.
Examples to replace common habits: ip addr (addresses), ip -br addr (concise view), ip link set dev eth0 up (toggle interfaces), and ip route (routing). Administrators also gain advanced features like policy routing and namespace-aware operations.
Switching from iwconfig to iw for wireless tooling
iwconfig depended on Wireless Extensions, deprecated in favor of nl80211. iw is the modern utility, aligned with cfg80211.
Try iw dev (list devices), iw dev wlan0 link (current connection), and iw list (capabilities). It supports contemporary standards like 802.11ac and 802.11ax and handles regulatory domains more reliably.
Replacing scp with sftp or rsync for safer file transfers
scp’s legacy protocol and path parsing quirks have bitten users and auditors alike. OpenSSH maintainers shifted scp to use SFTP under the hood by default starting in 9.0, steering users to safer patterns.
Use sftp user@host for interactive sessions or rsync -az –info=progress2 source user@host:/path for efficient, resumable transfers. For scripted copies, prefer sftp -b batchfile or rsync with SSH keys and strict host key checking.
Use grep -E and grep -F instead of egrep and fgrep
GNU grep folded the egrep and fgrep functionality into grep years ago. Recent GNU grep releases display obsolescence warnings for egrep/fgrep, signaling their retirement.
Drop-in replacements: grep -E ‘foo|bar’ for extended regex and grep -F ‘literal*string’ for fixed strings. Scripts become clearer and avoid future breakage.
Replacing netstat with ss for faster socket inspection
Like ifconfig, netstat is part of net-tools. ss is the netlink-native replacement that is faster and exposes richer socket data.
Common mappings: ss -tulpn (list listening sockets with PIDs), ss -s (summary), ss -tnp state established (active TCP). Expect quicker output on busy hosts and more precise filtering.
Moving from route to ip route for modern routing tasks
route struggled with IPv6 and complex policies. ip route is the canonical router interface in userland now, tightly aligned with kernel routing tables.
Typical commands: ip route show, ip route add default via 192.168.1.1, ip rule add fwmark 1 lookup 100 for policy routing. These tools simplify advanced networking without add-on hacks.
Switching from arp to ip neigh for neighbor table control
arp administered the ARP cache in IPv4-only contexts. ip neigh manages neighbor tables for both IPv4 and IPv6 and supports Neighbor Unreachability Detection for faster failure detection.
Examples: ip neigh, ip neigh show dev eth0, ip neigh flush all. For troubleshooting latency or failover, the extra state detail is invaluable.
How to Migrate Without Breaking Scripts and Builds
Audit your estate first. Use grep -R to find egrep, fgrep, ifconfig, netstat, route, arp, iwconfig, and scp in scripts and playbooks. Replace with the equivalents above and add comments describing the change.
Install the right packages: iproute2 and iw are standard on most distributions; OpenSSH clients provide sftp; rsync is widely available. CI images often omit net-tools by design, so modernizing reduces build friction.
Lint shell with ShellCheck to catch deprecated commands and unsafe scp patterns. For short-term compatibility, you can define aliases such as alias ifconfig=’ip -br addr’ or wrapper functions, but remove them once migrations are complete.
The terminal evolves. Moving to ip, iw, sftp, rsync, grep -E/-F, ss, ip route, and ip neigh delivers better security, performance, and fidelity with the Linux kernel—without waiting for the next outage to force the change.

