If your phone’s LTE data suddenly stops working, you’re not alone. As carriers sunset 3G and rely on LTE as the backbone for voice and data, short outages, handoff hiccups, and misconfigured settings can leave even flagship phones offline. Industry analyses by GSMA and Opensignal suggest LTE continues to account for a majority of mobile traffic worldwide — well over 60% in many markets — so when it flounders, day-to-day services feel the pain immediately.
The good news: the vast majority of LTE failures can be attributed to transient registration glitches, network mode mismatches, or a provisioning issue that you can rectify in minutes. So what to do? Here is how to get back online quickly, as well as the deeper checks that experts perform before recommending that you call your carrier.
- Start With Quick Resets To Restore LTE Connections
- Check Network Modes And Bands For Reliable LTE
- Examine SIM And eSIM Provisioning For LTE Service
- Check Carrier And Account Status For LTE Outages
- Review Phone Settings That Can Crush LTE Data
- Last But Not Least: Reset Network Settings
- When It Is Hardware Or Coverage Causing The Issue
Start With Quick Resets To Restore LTE Connections
Turn airplane mode on and off for 10–20 seconds. This causes the modem to forget about stale sessions and re-register with the tower. It’s a cellular version of pulling and plugging the cable back in — and it fixes an enormous proportion of LTE stalls.
If that doesn’t work, try rebooting your phone. A full restart will clear the cached radio states and reset carrier settings. To be safe, open a few sites or a maps app after boot rather than trusting one speed test to tell you that you’re properly connected over LTE.
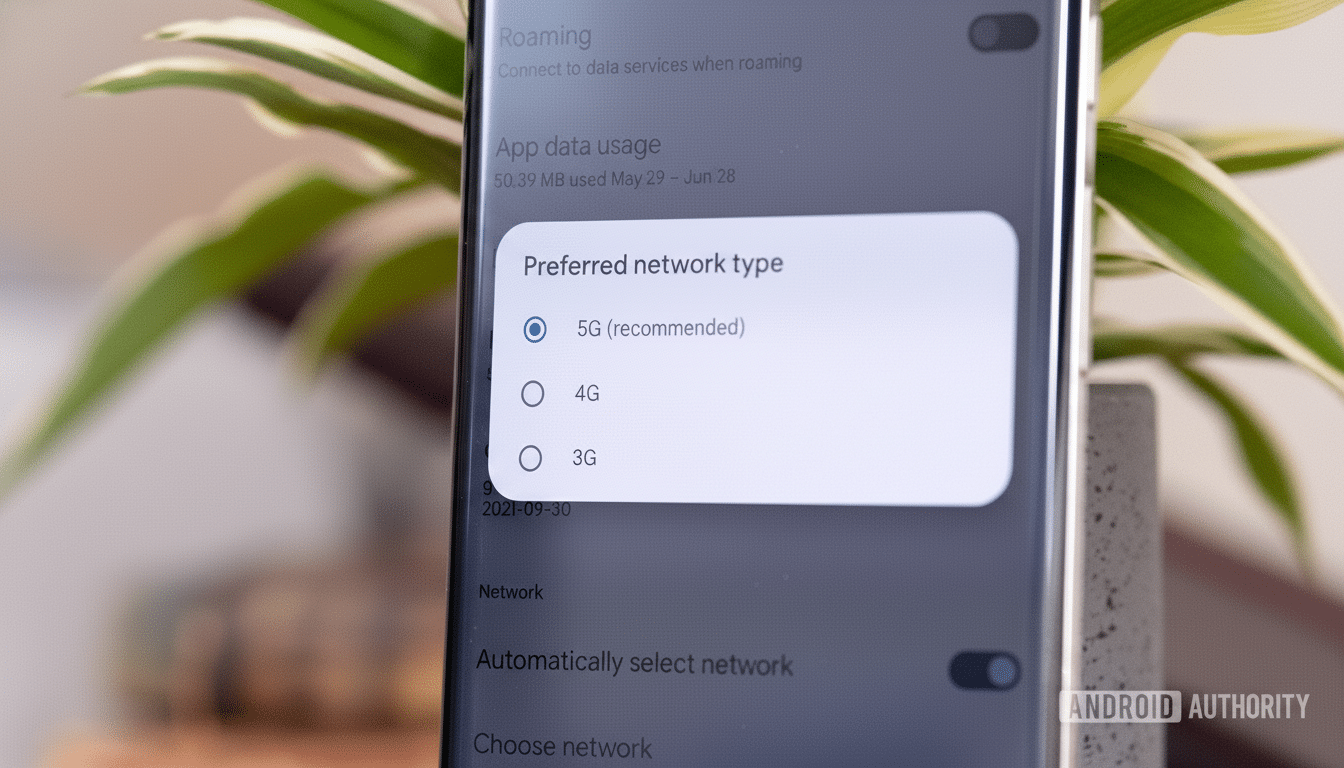
Check Network Modes And Bands For Reliable LTE
Verify your device is configured to support LTE. On Android, go to Settings > Network or Mobile Network and look for 5G/4G/3G Auto or something similar in the list of options. On iPhone, open Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Voice & Data and ensure LTE is enabled.
If your phone can’t decide between an unreliable 5G signal and LTE, then turn off 5G for now and force a solid LTE connection.
Some of these issues have shown up in Opensignal’s data: the company has analyzed performance and observed that some NSA 5G–LTE handovers result in erratic performance in different locations; switching to a stable LTE connection can restore consistent reliability.
Examine SIM And eSIM Provisioning For LTE Service
Reseat your SIM: power off, pop the tray out, clean any dust with a lint-free cloth, and reseat carefully. Dual-SIM phones can have LTE on only one slot at a time — convertible devices switch between them for LTE. For eSIM, request that your carrier reprovision; they can initiate a fresh activation or send you a new QR code.
Confirm VoLTE is provisioned. Without it, some carriers could restrict data or voice traffic. These might appear, on Android, as a VoLTE or 4G Calling toggle in the Mobile Network settings. For iPhone, verify that LTE is enabled for Voice & Data. If you don’t see these options, your carrier provisioning may not be finished.
Check Carrier And Account Status For LTE Outages
Before diving into the deep end, eliminate any network-bound problem if possible. Refer to your carrier’s outage page or popular monitoring services. Even with full signal bars, LTE can go down regionally after storms, maintenance windows, or fiber cuts.
Then check your plan. Exceeding a high-speed data cap may lead to throttling or temporarily blocked hotspot traffic. MVNOs can also be deprioritized during congestion, so your slowdown might just look like LTE gone AWOL. Contact support to “refresh” your line, re-enable data, or confirm APN settings connected to your account.
Review Phone Settings That Can Crush LTE Data
Data Saver, Low Data Mode, or per‑app restrictions can quietly block background connections. On Android, see if Data Saver is enabled and that your essential apps are whitelisted. If LTE appears erratic on iPhone, turn off Low Data Mode in the Cellular Data Options.
If a provider has outages or blocks, VPNs and Private DNS can also disrupt LTE. You could temporarily disable the VPN, set DNS to automatic, and try again. If you’re traveling, make sure Data Roaming is enabled and that Network Selection is set to automatic so the phone can latch on to partner networks.
Last But Not Least: Reset Network Settings
A network reset can make it much clearer when settings have gone wonky after an update or SIM swap. On Android that’s under Settings > System > Reset options > Reset Wi‑Fi, mobile, and Bluetooth. On iPhone, navigate to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset > Reset > Reset Network Settings. You’ll have to reenter saved Wi‑Fi and Bluetooth pairings, but LTE should — caveat that this can be a bit of voodoo — often return after the restart.
When It Is Hardware Or Coverage Causing The Issue
Dropping a hammer or immersing in water will break antennas or the modem, leaving you with one-bar LTE that never moves data. Compare your performance with that on another SIM or on a different phone using the same network in the same spot. If it’s an outlier, make a diagnostic or warranty claim.
It could also be indoor coverage that is the actual issue. Even on parts of the map that the FCC says are covered, mid-band and high-band signals often have difficulty penetrating solid objects like concrete and metal. Try making a call via Wi‑Fi, get closer to a window, or test it outside; if LTE returns to normal, figure out how to enable Wi‑Fi Calling permanently or use a carrier-supplied signal booster.
If none of the above works, call your carrier and have them check line provisioning, IMS registration, APN settings, and try to reprovision the SIM or eSIM. Most LTE “mysteries” sit firmly on one of those levers — easy to correct once the right system switch is flipped.

