Google is quietly prepping a wave of Gemini Live upgrades, with new Labs toggles discovered inside the Google app hinting at capabilities that push the assistant toward true phone-level agency. References spotted in version 17.2.51.sa.arm64 point to experimental features like multimodal memory, improved noise handling for voice, screen-aware responses, a deliberative “Thinking” mode, and deeper research tools — all individually opt-in.
What the New Labs Toggles Reveal About Gemini Live
Internally tagged to Google’s recurring “robin” codename for Gemini, the strings call out Live Experimental Features and a Live Thinking Mode alongside two agentic options: Deep Research and UI Control. The description for Live Experimental Features mentions four pillars: multimodal memory, better noise rejection, the ability to respond to what it “sees” on your screen, and results personalized by your Google apps.
- What the New Labs Toggles Reveal About Gemini Live
- Live Thinking Mode Could Slow Down To Get Smarter
- From Assistant To Agent UI Control On Phones
- Deep Research Targets Long-Context, Multi-Step Tasks
- On-Device Experience and Audio Upgrades in Gemini Live
- Availability and What to Watch as Features Roll Out

The Live Thinking Mode suggests a version of Gemini Live that takes more time to reason before responding. Separately, Deep Research appears designed to handle complex, multi-step inquiries, while UI Control explicitly describes the assistant acting on your phone’s interface to complete tasks. A small interface preview within the app even shows a “Thinking…” state and a “GL – Exp” label, signaling that these experimental flags can be enabled individually.
Live Thinking Mode Could Slow Down To Get Smarter
Deliberative response modes trade speed for depth — a pattern AI researchers have used to boost accuracy on reasoning-heavy prompts. Google previously split its assistant workflow between faster, lighter models and slower, more analytical pathways. Bringing that approach to Gemini Live would let users pick what matters in the moment: rapid back-and-forth for casual tasks, or a slower, more rigorous pass for nuanced questions.
Think of itinerary planning during a voice call: a fast mode might list a few options quickly, while a thinking mode could reason through timing, traffic, and your calendar, then propose a schedule with alternative routes and booking reminders. Expect modest latency increases in exchange for more structured, source-aware answers.
From Assistant To Agent UI Control On Phones
UI Control is the most transformative detail. Rather than merely describing steps, an agent could tap, scroll, and fill fields on your behalf — booking a rideshare after checking your calendar, adjusting phone settings during a call, or triaging email with labels and follow-up tasks. This aligns with Google’s assistant-as-agent vision teased in Project Astra, where models “see” context and act across apps.
Practical deployment will hinge on granular permissions, clear on-screen confirmations, and revocable scopes. Expect guardrails similar to Android Accessibility and system automation APIs, with visible prompts before the assistant performs sensitive actions like purchases, location sharing, or account changes.
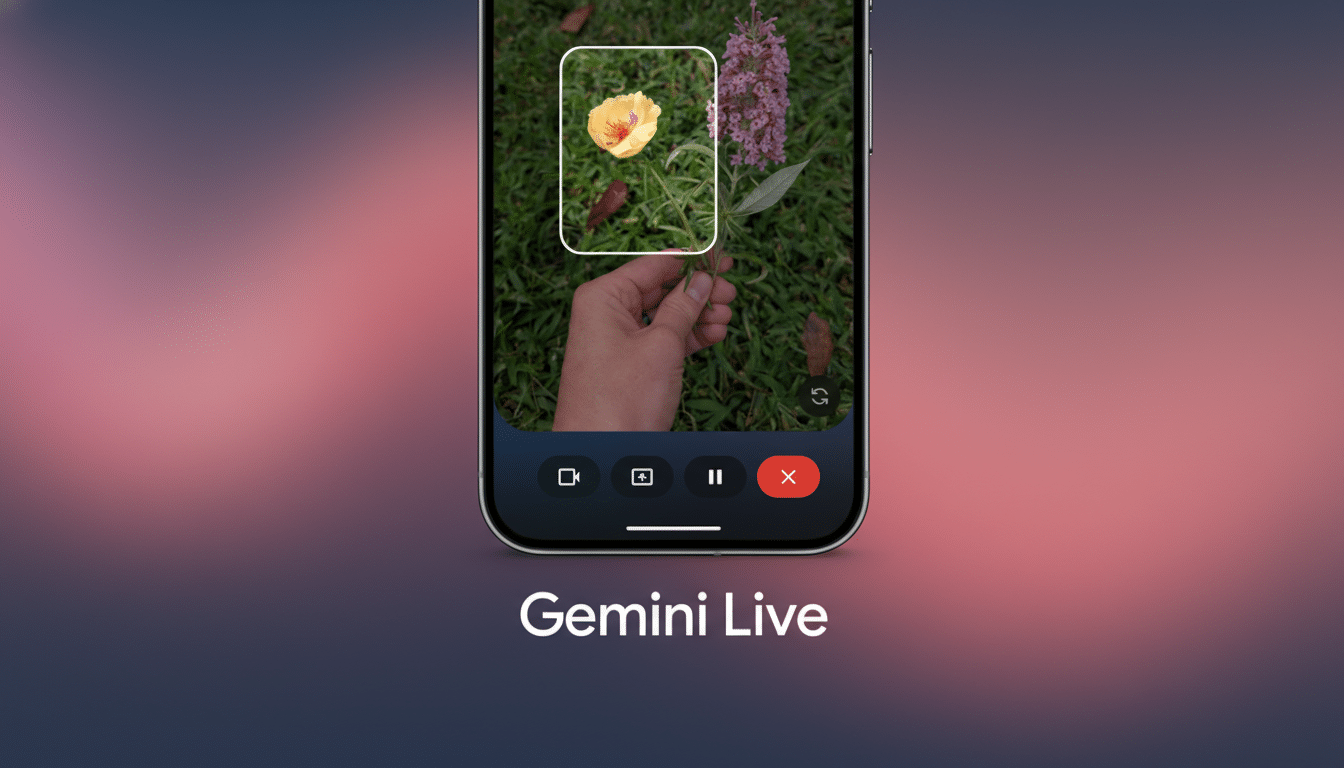
Deep Research Targets Long-Context, Multi-Step Tasks
Deep Research points to long-running, multi-step tasks that synthesize information across sources and formats. Google’s work on long-context models — including previously announced 1 million-token context windows in Gemini 1.5 Pro — shows how an assistant can juggle large documents, notes, and screenshots without constantly losing the thread. A Labs version of Deep Research could automatically gather materials, draft structured findings, and return updates as progress is made.
This is the difference between “summarize this page” and “map out the pros and cons of three degree programs based on my budget, commute, and past coursework, then prepare application checklists.” It’s not just retrieval; it’s orchestration.
On-Device Experience and Audio Upgrades in Gemini Live
The Live features also highlight real-time polish. Better noise handling is essential for hands-free use in cars or crowded spaces, and screen-aware responses would let Gemini Live immediately reference what’s on display — from a boarding pass to an error dialog — without manual copy-paste. Multimodal memory suggests the assistant can carry details across voice, text, and visuals, retaining context between sessions while respecting user privacy settings.
Google has demoed near-real-time perception and response in past showcases, and these toggles imply that polish is moving into user-facing trials. Expect a blend of on-device speech and vision components with cloud inference for heavier reasoning, tuned to keep latency low enough for natural conversation.
Availability and What to Watch as Features Roll Out
Despite the strings appearing in the app, the Labs icon is not yet active for most users, and the controls remain hidden behind server-side flags. The structure suggests Google will let users opt into individual experiments rather than a single all-or-nothing switch — a smart approach for testing safety, reliability, and battery impact.
Given Google’s track record, expect staged rollouts, region gating, and A/B testing before wider availability. If and when these Labs features land, they could mark a shift from conversational assistant to capable on-device agent, with Gemini Live becoming not just faster and more context-aware, but fundamentally more useful.

