Google quietly ushered a small group of reporters into its most closely guarded Pixel Hardware Labs, offering an unusually candid look at how the company stress-tests, tunes, and designs its phones. Tucked inside a single facility with more than fifty specialized labs, the tour pulled back the curtain on the decisions and instruments that shape how a Pixel feels in your hand, sounds in your ear, and survives life in your pocket.
Inside the reliability gauntlet for Pixel phone testing
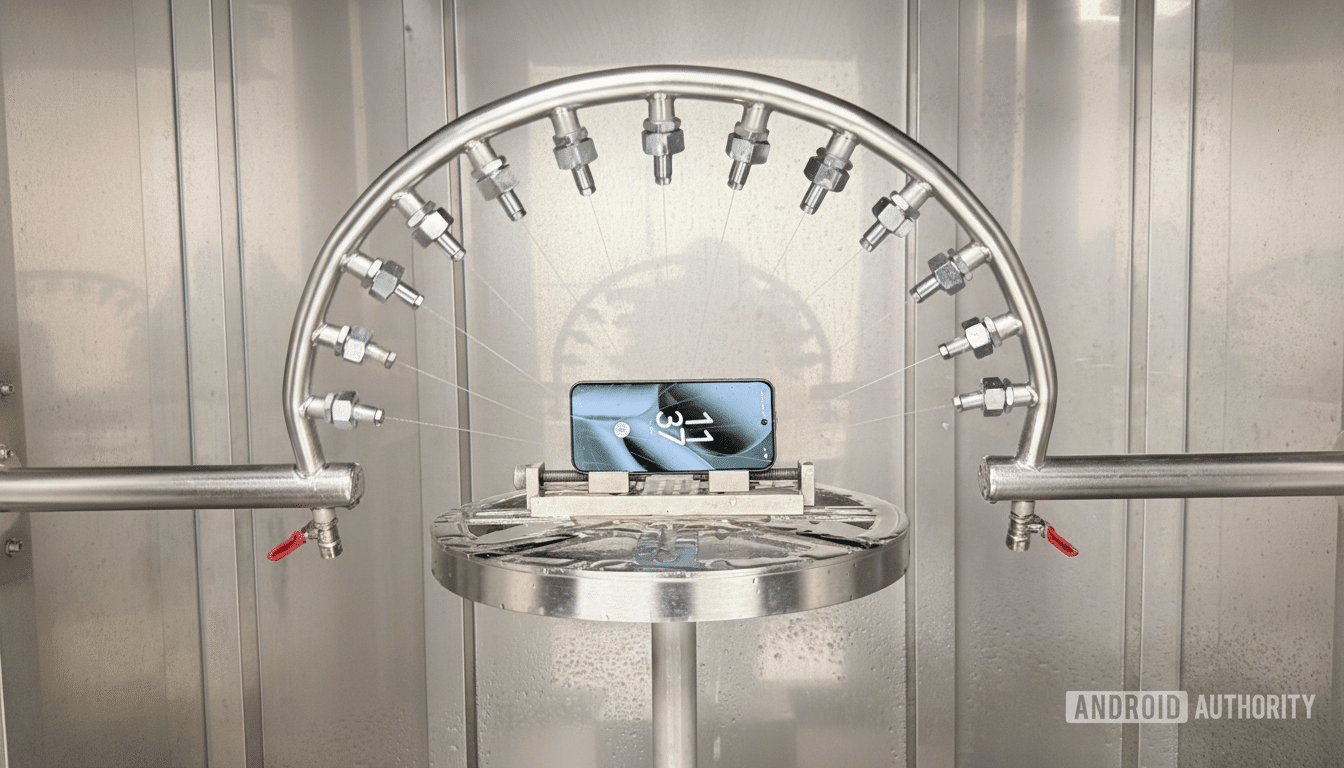
The visit began in a durability suite where engineers try to break devices so customers don’t. One station simulates IPX4 exposure with a rotating spray rig that pelts active phones from every angle, checking for display glitches and moisture ingress. Flagships that carry an IP68 claim must also pass full-immersion trials under the IEC 60529 standard, a separate phase designed to validate both dust-tight sealing and resistance to prolonged submersion.
From there, the tests get unapologetically real-world. A “sit test” uses a calibrated, humanlike posterior to mimic the force of someone plopping down with a phone in a back pocket, a scenario that has quietly bent frames across the industry. Impacts are mapped too: steel and polymer spheres are dropped at controlled heights onto the front and back glass, while multi-angle drop rigs slam phones against different surfaces to study how frames, adhesives, and internal components dissipate shock.
Foldables face their own trial by repetition. The Pixel 10 Pro Fold runs on a cycle machine that opens and closes the device until the hinge and flexible display prove they can withstand 200,000 folds—roughly equivalent to years of daily use for most people. Rounding out the regimen is a tumble test that spins phones with keys, coins, and other bag-bottom hazards to emulate months of scuffs and knocks in minutes.
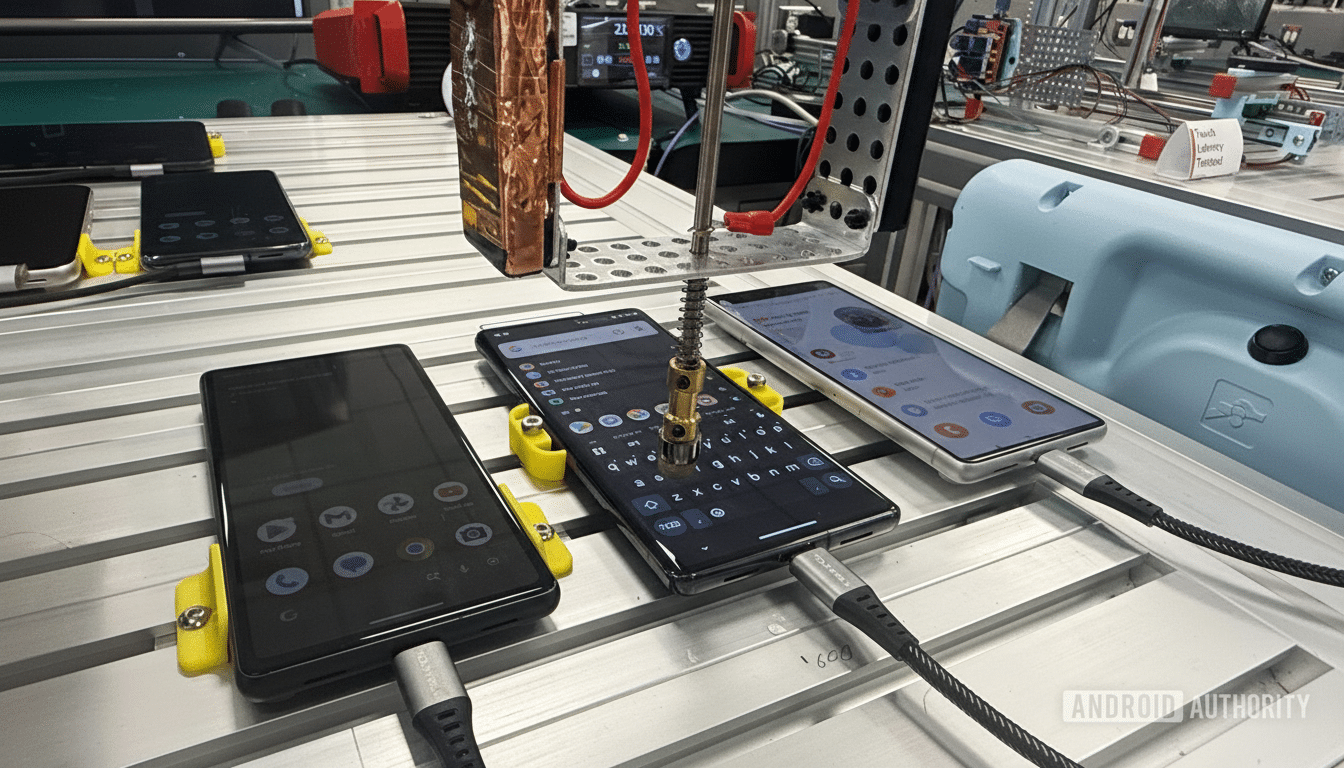
How robots validate everyday magic in Pixel features
In the robotic connectivity lab, articulated arms quietly choreograph thousands of actions a day. Custom 3D-printed fixtures hold devices at precise angles while instruments probe touch latency, proximity sensing, ambient light behavior, and thermal responses. It’s where invisible polish happens: Watch Unlock must handshake with a wearable reliably, Adaptive Brightness must feel instant yet stable, and motion-driven gestures like Flip to Shhh must trigger without false positives.
Many of these checks are built on industry baselines from bodies like 3GPP and CTIA, but Google’s rigs are tuned for Pixel-specific behaviors. The goal isn’t just passing a spec—it’s achieving consistency across countless edge cases, from a pocketed phone waking correctly to radios managing handoffs without stutters in crowded networks.
Inside sound labs that tune calls and Pixel features
Two cavernous anechoic chambers—rooms engineered to eliminate echoes and outside noise—anchor Google’s audio validation. Here, engineers quantify microphone beamforming, wind suppression, and speaker tuning, then iterate until they hit targets for clarity and loudness. Call quality scenarios are measured with standardized methods, including ITU algorithms such as POLQA, to verify that voices cut through urban noise or office hum at different hold positions.

The team also refines feature-level experiences. Audio Zoom, available since the Pixel 5 era, is stress-tested by steering microphone arrays at distant subjects while intentionally injecting background clatter to ensure clean separation. Real-time voice translate workflows are evaluated for timing and intelligibility, so speech stays natural even as on-device models work in the background.
Design Lab Shapes Foldables And Thermals
Down the hall, the design lab is where sketches harden into manufacturable ideas. One standout: the gearless hinge in the Pixel 10 Pro Fold. By swapping traditional gears for cam-based mechanics, engineers carved out space for a larger folding display while keeping the chassis slim and freeing volume for a bigger battery—an elegant solution to competing constraints.
Materials science plays a starring role. Precision rigs stretch polymers and metals far past everyday strain to predict long-term wear on phone frames, watch bands, and coatings. On thermal management benches, vapor chambers, graphite sheets, copper foils, and pastes are mixed and matched to move heat away from chips and modems. Lessons learned here have appeared across recent Pixel generations, including the Pixel 8, 9, and 10 families, where sustained performance under load is increasingly a design requirement, not a luxury.
Why this rare peek into Pixel labs matters now
Every major phone maker runs drop tests, audio checks, and design experiments behind closed doors. What set this visit apart was the degree of customization—fixtures built in-house, software tuned for corner cases, and cross-lab loops that carry a finding from a robot arm straight into a design tweak. It’s the kind of infrastructure that explains why a feature you never see advertised—like consistent pocket detection or more stable brightness shifts—can make a device feel quietly refined day after day.
If nothing else, the tour made clear that delightful phone moments don’t happen by accident. They’re engineered, validated, and re-engineered across dozens of rooms where perfection looks like boredom: a hinge cycling for the thousandth time, a microphone chasing a cleaner signal, a touchscreen tapped by a robot until it stops surprising anyone. That’s the unglamorous path from lab secret to daily habit—and the reason these labs matter long before a Pixel reaches your hand.

