OpenAI is rolling out ChatGPT-health/” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener noreferrer”>ChatGPT Health, a new mode designed to give safer, more personal medical guidance by grounding answers in your own health data — and it’s free to try as access expands. The experience lives inside ChatGPT, but runs in a dedicated health space that can securely draw on your medical records and wearable data to make advice more relevant to your situation.
The aim isn’t diagnosis or treatment. Instead, it’s to help you prepare for appointments, track patterns across labs and symptoms, and make sense of the steady stream of information that most patients juggle across portals, apps, and notes. OpenAI says roughly 40 million people a day already ask ChatGPT health questions; this feature is meant to make those exchanges more accurate and context-aware.
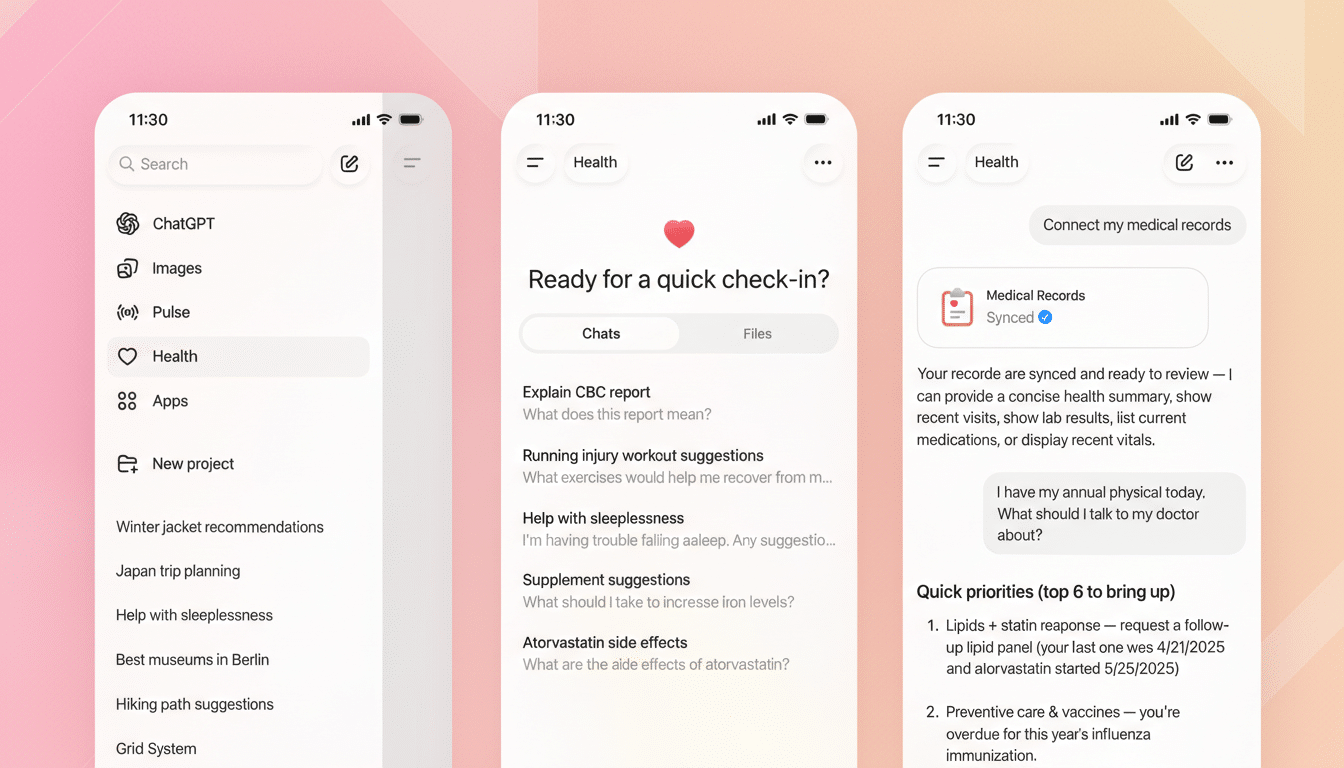
What ChatGPT Health Does and How It Supports Patients
ChatGPT Health lets you connect sources like patient portals, lab results, pharmacy summaries, and compatible wearables so the model can reference your history while answering everyday questions. Think: summarizing your latest lab panel in plain language, flagging whether a new symptom fits past patterns, or drafting a checklist of questions to ask your clinician.
Crucially, it’s not a replacement for medical care. OpenAI positions the tool as a personal health companion that helps you understand options, articulate goals, and navigate care more confidently — especially when information is scattered across systems that don’t talk to each other.
Because it can see longitudinal data, ChatGPT Health can spot trends you might miss: rising A1C over six months, blood pressure variability tied to poor sleep, or medication adherence gaps visible in refill history. It can then suggest topics to raise with your clinician, backed by your own numbers.
How to Use It for the Best Advice and Safer Guidance
Join the waitlist inside ChatGPT and, once enabled, choose Health from the sidebar. Connect the health sources you’re comfortable sharing. You’ll get more tailored responses if you include recent labs, medication lists, allergies, major diagnoses, and data from wearables like heart rate, sleep, and activity.
Ask targeted questions with context. For example: “Given my A1C of 7.6, current metformin dose, and average daily steps, what questions should I ask my doctor about adding a GLP‑1?” or “Based on my sleep and heart rate trends, how could I adjust my marathon training without overreaching?”
Request structured outputs you can act on: “Create a one‑page briefing I can share with my cardiologist,” “Turn this into a pre‑op checklist,” or “List pros and cons of two options and what monitoring I’d need.” Ask it to reference reputable guidance (for instance, national guidelines or public health agencies) and to highlight uncertainties or red flags that warrant in‑person care.
Use it between visits to stay organized. Have it track questions over time, translate medical jargon into plain language, and compare new results against your baseline. When in doubt, have it draft a secure message to your care team so you can confirm next steps.

Privacy and Safety Built In for Your Health Data
OpenAI says health conversations and files are encrypted at rest and in transit, and the Health mode adds extra isolation so data stays compartmentalized from your other chats. The company also states that Health conversations will not be used to train its foundation models.
The health space acts as its own memory, keeping connected apps and files separate from your general ChatGPT history. Even so, remember that this is not your hospital’s portal. Treat it as a powerful assistant, not a medical record custodian, and only connect what you’re comfortable sharing.
Does It Actually Help Patients Make Better Decisions
Evidence suggests AI can add value in health Q&A when used prudently. In a JAMA Internal Medicine study, licensed clinicians judged ChatGPT’s responses to patient questions as higher quality and more empathetic than physician replies in 79% of cases — while also emphasizing the need for clinical oversight. Public health bodies, including the World Health Organization, advise that AI health tools be used with transparency and human review.
Real‑world example: A patient with type 2 diabetes and hypertension connects labs, meds, and smartwatch data. ChatGPT Health summarizes trends, notes that morning blood pressures rise on days after short sleep, and drafts three evidence‑based questions to discuss medication timing and sleep hygiene at the next visit. No diagnosis, just focused, data‑aware preparation.
Limitations remain. AI can misinterpret incomplete records, reflect biases in training data, or give overconfident answers. The safest pattern is to use it for education, organization, and decision preparation — and to loop in your clinician for care decisions.
Who Can Try It Now and When Access Will Expand
Access starts with a waitlist as OpenAI refines the experience. The company says it will expand to all users on the web and iOS in the coming weeks. When you get access, select Health in the ChatGPT sidebar to begin.
The headline news for consumers: ChatGPT Health is free to use as it rolls out. If you already rely on AI for quick health questions, this dedicated mode is likely the best way to get more accurate, personally relevant guidance — with your own data doing the heavy lifting and your clinician still at the center of care.

