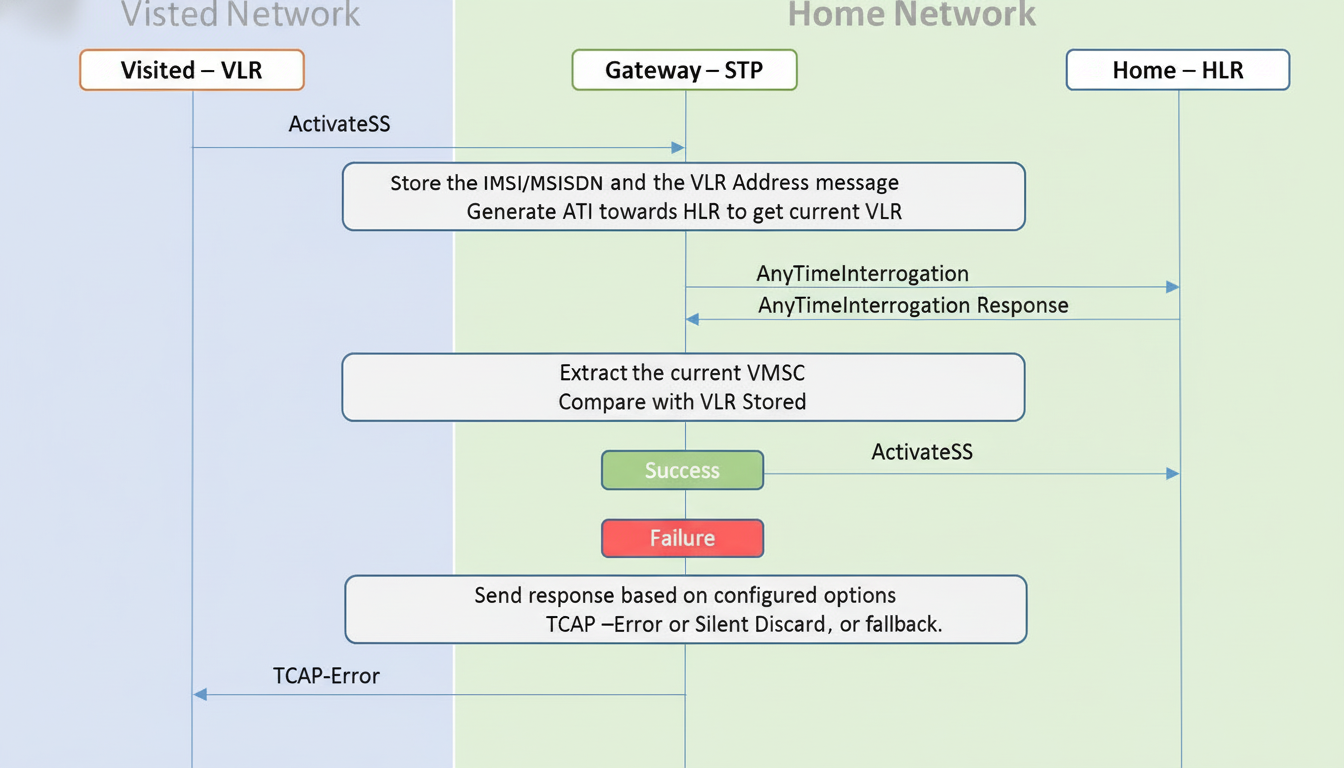
Complexation any time interrogation (ATI) is a known process in the field of digital communications and forensics. From telecommunications, to criminal justice, to cybersecurity, ATI is a valuable tool that enables authorities and corporations to obtain important information at any time. In this post, we’ll explain what ATI is, how it’s used, where it’s not, and the pros and cons of using it.
What Is Any Time Interrogation (ATI)?
Any Time Interrogation (ATI) is a method to obtain access to, retrieve or monitor data at all times, for example without having to wait for pre-scheduled updates. Typical usage of ATI is in telecommunication networks, where it provides the ability to check the status, location, or activity of a mobile subscriber in real-time.

The idea is straightforward – rather than logging data and then spending a few days to get any meaningful work out it, ATI is designed to make it possible to ‘interrogate’ the data right away when you need it.
How ATI Works
ATI works on the concept of short term data retrieval. The process can include any of the following, depending on the system:
- The request – A signal is transmitted to a DB or network system demanding the most up-to-date information.
- Real-time data – The system collects data from live records, not just stored logs.
- Results delivery – Requested information is provided to the authorized requestor as soon as it is available.
For instance, in mobile systems, ATI can be employed to verify the location of an apparatus, the last state of a user, or whether the apparatus is attached to the network or not.
Uses for Any Time Interrogation (ATI)
There are several industries in which ATI is applied. Here are a few of the most popular uses:
1. Law Enforcement
Police and intelligence services can employ ATI in surveillance operations, observing suspects, or regarding the position of individuals in the context of current investigations. It gives instantaneous access to information that might be essential in emergencies.
2. Telecommunications
The ATI is an essential feature in telecommunication systems, to control the portable terminal. Carriers can see if a phone is active, roaming or on a particular network at a particular time. This is necessary for debugging and user support.
3. Cybersecurity
ATI techniques can assist security specialists in identifying abnormal behavior within a network. Real-time querying can provide faster detection of deficiencies and reduces the risk of cyber-attacks.
4. Emergency Services
In addition, ATI can be used for finding mobile phones by emergency rescue teams. This is particularly useful in an emergency such as natural calamity, missing person, or health crisis.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Certain sectors may have specific regulatory requirements that data need to be kept accessible for an audit or investigation. ATI is able to provide a trusted approach for the HoNB to meet this kind of local requirements.
Advantages of ATI
The primary advantage of Any Time Interrogation is speed: By providing on-demand information, ATI replaces time lags with time savings and directly impacts decisions. Some benefits include:
- Instant access to current data.
- More accurate, as it describes the most current state of a system.
- Faster response time for police, fire and emergency services.
- Improved security monitoring – providing the ability to detect threats more rapidly.
Challenges and Concerns
As powerful a tool as ATI is, it also leads to some interesting questions and challenges:
1. Privacy Issues
ATI can find a person’s location or access sensitive information in the wrong hands of a government official, this raises questions of privacy rights. Critics worry that, in the absence of strict regulations, ATI could be abused for unsanctioned surveillance.
2. Legal Limitations
In some countries, ATI is restricted to be used by law enforcement or government authorities through a court order. Unauthorized use of ATI may lead to legal action.
3. Data Security
ATI equipment cannot be hacked. If hackers were to get in the door, they could also use the technology for nefarious ends.
4. Cost and Infrastructure
The deployment of ATI is complex and requires advanced infrastructure and know-how. It is often harder for smaller groups to justify paying for such secure systems.
ATI in the Modern World
ATI is advancing with technology. With increasing proliferation of 5G networks, cloud storage and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, the application space of ATI is growing rapidly. For instance:
- Telecom companies use ATI to power billions of devices globally.
- Smart cities might use ATI to track sensors, traffic and utility systems in real time.
- ATI Cyber security companies use ATI to protect critical infrastructure.
But that growth also means tighter regulation and ethical discussions are required to maintain state security while respecting personal rights.
The Future of Any Time Interrogation
And so now we live in an era in which any time questioning, any time learning, takes place, any psychology test given to linguistic minorities, turns out checking the ratio.
In the future, ATI may be even more interwoven in everyday life. Governments and industries are refining how ATI is utilized to keep it from becoming a blunt-force instrument while at the same time respecting privacy rights.
Key future trends may include:
- ATI – artificialy intelligence ATI could be used to filtering in real time a vast information to make right interrogation.
- Tougher restrictions: More countries are likely to introduce laws governing who can use ATI, and under what conditions.
- Encryption and security enhancements – In order to avoid abuse, ATI systems will require enhanced measures to establish unauthorized access.
Conclusion
ATI is the common process widely used in 3G/4G mobile communications, law enforcement investigations, and cyber defense. It increases efficiency, safety, and real-time decision-making through immediate access to data.
However, ATI also presents significant ethical and legal considerations, particularly with respect to the questions of privacy and security. The future role of ATI, as the benefits and costs of this technology unfold, will depend on achieving a balance between these two tendencies in our ever more interconnected world.
For now, ATI is a powerful weapon – one that, responsibly used, can make societies safer, networks more resilient, and services more dependable.

